FIG 2.
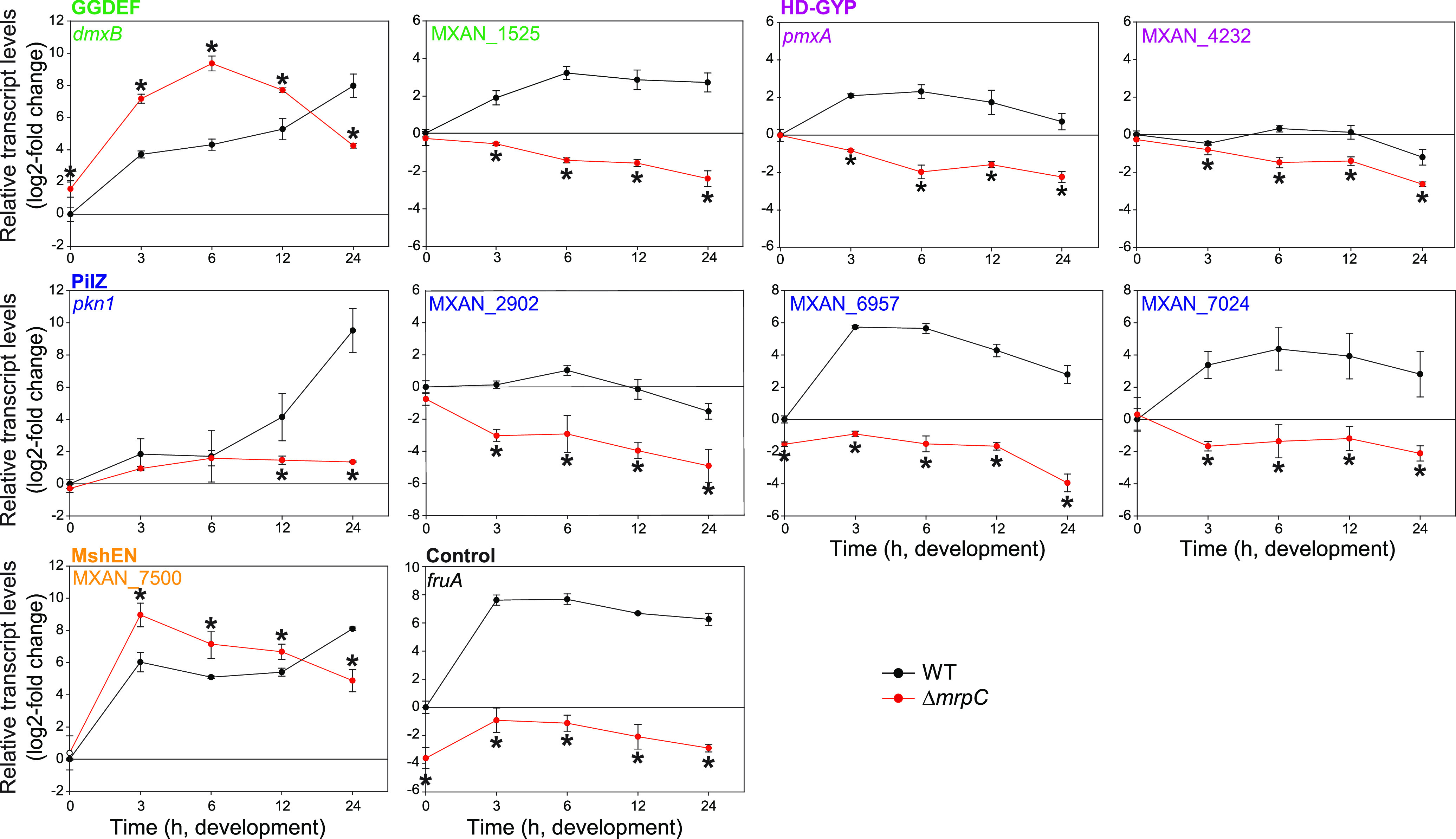
Regulation of the expression of genes encoding c-di-GMP-associated proteins by MrpC. Total RNA was isolated from cells developed in MC7 submerged cultures at the indicated time points from WT (black) and the ΔmrpC mutant (red). Transcript levels were determined using RT-qPCR and are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) from two biological replicates, each with two technical replicates, relative to WT at 0 h. *, P < 0.05; Student’s t test in which samples from the ΔmrpC mutant were compared with the samples from WT at the same time point. fruA served as a positive control. Based on protein sequence analysis, MXAN_1525 and MXAN_4232 are predicted to have DGC and PDE activity, respectively; however, neither a ΔMXAN_1525 nor a ΔMXAN_4232 mutant has defects during growth or development (37, 40). pkn1, MXAN_2902, MXAN_6957, and MXAN_7024 are PilZ domain proteins; however, none contain the conserved motifs for c-di-GMP binding (27, 36). Except for Pkn1, a lack of any of these four proteins does not cause defects during growth or development (36, 60). MXAN_7500 is a MshEN domain protein with the sequence motifs for c-di-GMP binding (17); however, it is not known whether this protein binds c-di-GMP or whether it is important during growth and development.
