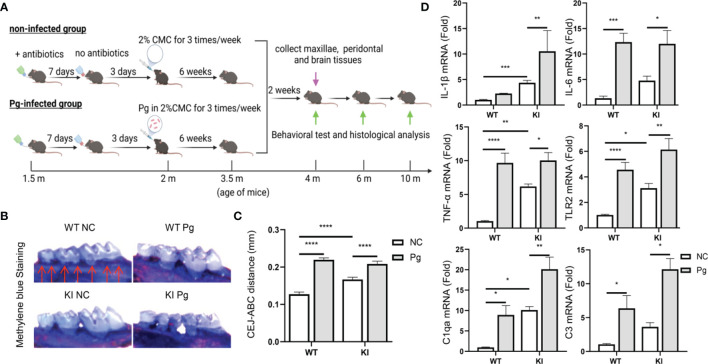
Figure 1.
Pg-induced alveolar bone loss and periodontal inflammation in App KI and WT mice following oral infection. (A) Schematic of the experimental design used in this study. m, month. (B) Representative methylene blue-stained maxillae from non-infected (NC) and Pg-infected WT and App KI mice (n=9 mice/group). Bone loss was assessed in a total of 7 buccal sites (red arrows) per mouse. (C) Alveolar bone loss in Pg-infected and non-infected WT and App KI mice; mm, millimeter; CEJ-ABC, cemento-enamel junction-alveolar bone crest. (D) Inflammatory cytokine and complement gene expression in gingival tissues from non-infected and Pg-infected WT and App KI mice. Gene expression was normalized to GAPDH and expressed as fold changes. Samples were done in duplicate (n=7 mice/group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, by two-way ANOVA followed with Tukey correction.