Figure 1.
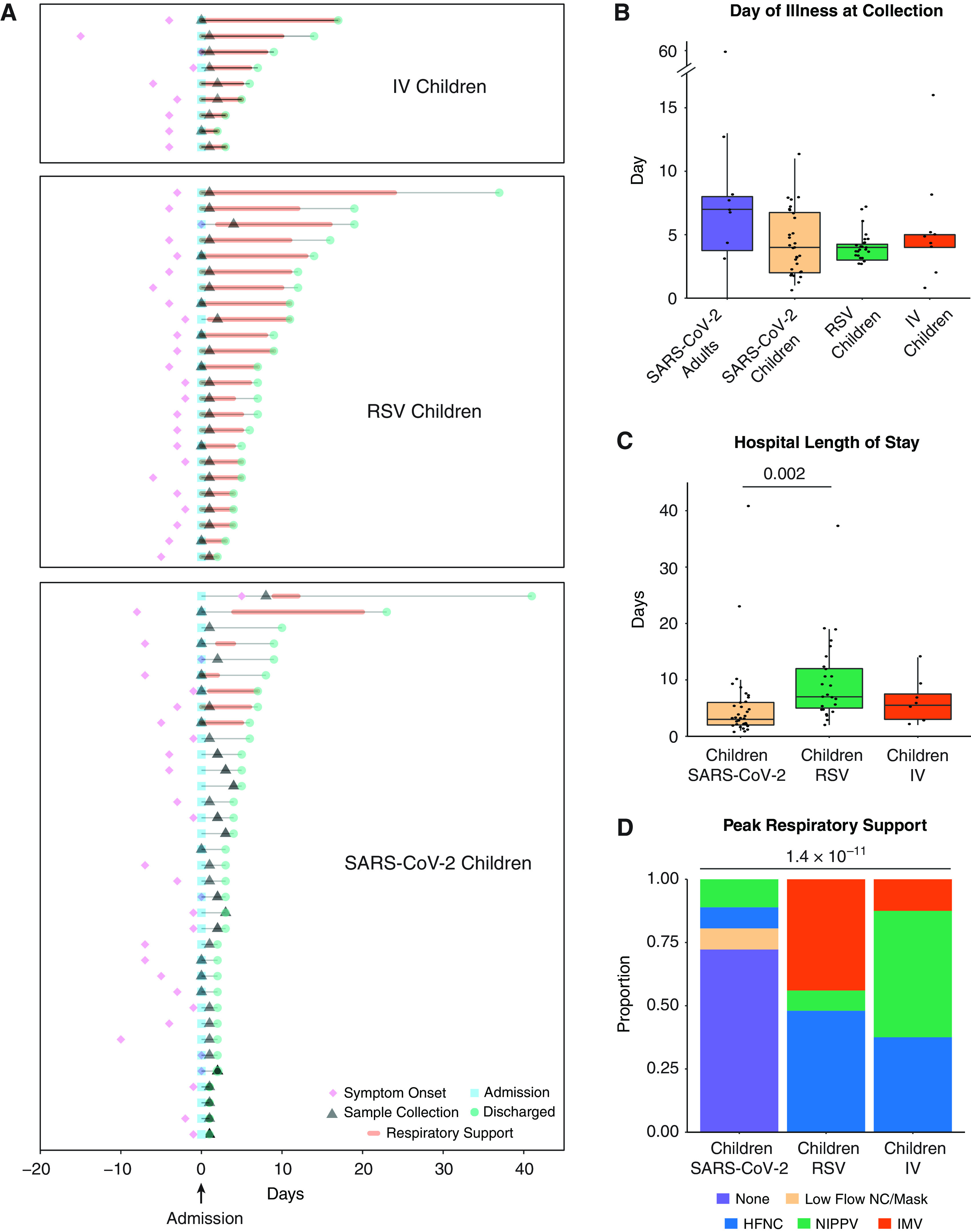
Description of the cohort. (A) Clinical course of pediatric participants. Timing of symptom onset (diamond), admission (square), sample collection (triangle), discharge (circle), hospital stay (thin line), and duration of advanced (HFNC, NIPPV, or IMV) respiratory support (bold line) of hospitalized children with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (n = 36), RSV (n = 24), and IV (n = 9). (B) Self- or parent/guardian-reported time since symptom onset at the time of sample collection was similar between all participant groups. Pairwise comparisons of medians performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Children with RSV infection had a longer hospital length of stay than children with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Pairwise comparisons of medians performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. (D) Higher proportions of children with IV and RSV infection required HFNC, NIPPV, and IMV at peak illness severity when compared with children with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Proportions compared using Fisher’s exact test. All P values were adjusted using Benjamini-Hochberg FDR correction. Differences were not significant (P-adjusted > 0.05) unless noted. FDR = false discovery rate; HFNC = high flow nasal cannula; IMV = intermittent mechanical ventilation; IV = influenza virus; NIPPV = noninvasive positive pressure ventilation; RSV = respiratory syncytial virus.
