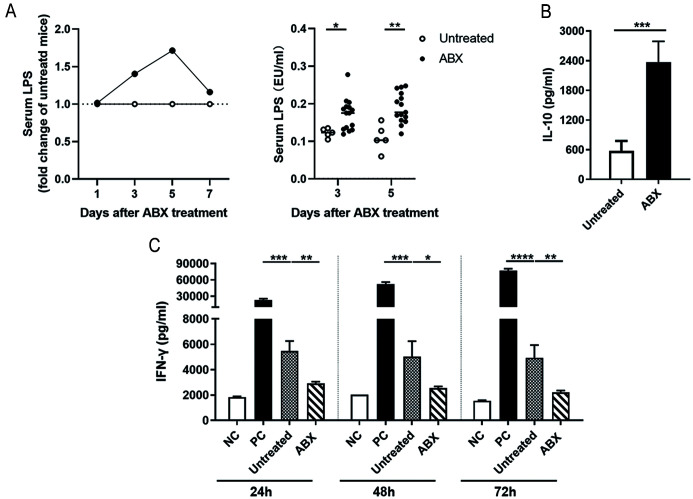
Fig. 1. Gut microbiota sterilization by antibiotics results in increased serum LPS levels and enhanced IL-10 production and T cell suppression of KCs.
(A) C57BL/6 mice were treated with antibiotics (ABX; ampicillin, neomycin, metronidazole, and vancomycin) in drinking water (ABX, n=15; Untreated, n=5) and the kinetics of serum LPS were monitored by ELISA. (B) KCs were purified from the liver of mice 30 days post-ABX treatment and cultured in vitro. After a whole night, the amount of IL-10 in the culture supernatant was determined by ELISA. (C) KCs were co-cultured with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 (1 µg/mL)-stimulated splenocytes from naïve mice at a ratio of 1:2 (KCs:splenocytes [SPLs]). After 24, 48 and 72 h, the amount of IFN-γ in the culture supernatant was determined by ELISA. Anti-CD3/anti-CD28-stimulated SPLs were used as a positive control (PC) and unstimulated SPLs were used as a negative control (NC). Unpaired t-test was applied. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; KCs, Kupffer cells.