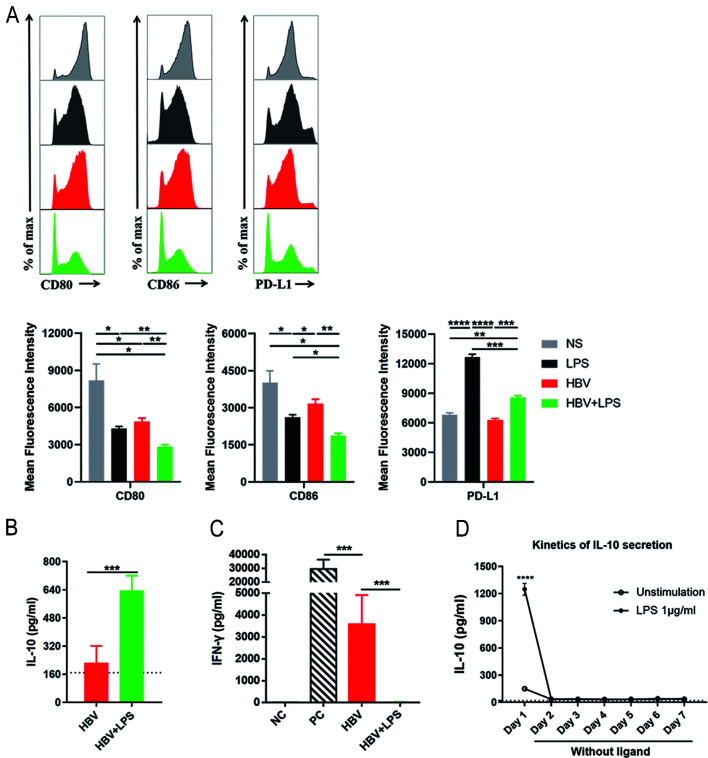
Fig. 2. LPS stimulation induces strengthened suppressive phenotype, enhanced IL-10 production and T cell suppression of KCs in HBV-replicating mice.
C57BL/6 mice were subject to HDI with the NS, LPS, pAAV/HBV1.2 plasmid in combination with LPS (HBV+LPS) or not (HBV). After 3 h, KCs were purified from the liver of those mice. (A) CD80, CD86, and PD-L1 expression on KCs were analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) KCs were purified and cultured in vitro. After a whole night, the amount of IL-10 in the culture supernatant was determined by specific ELISA. (C) KCs were co-cultured with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 (1 µg/mL)-stimulated SPLs at a ratio of 1:2 (KCs:SPLs). After 48 h, the amount of IFN-γ in the culture supernatant was determined by specific ELISA. Anti-CD3/anti-CD28-stimulated SPLs were used as a PC and unstimulated SPLs were used as an NC. (D) KCs were stimulated by 1 µg/mL LPS for 24 h (day 1), washed, and cultured for another 6 d without stimulation. Culture medium was changed every 24 h. IL-10 secretion by KCs was determined by ELISA. Unpaired t-test was used. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HDI, hydrodynamic injection; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; KCs, Kupffer cells; PC, positive control; SPLs, splenocytes.