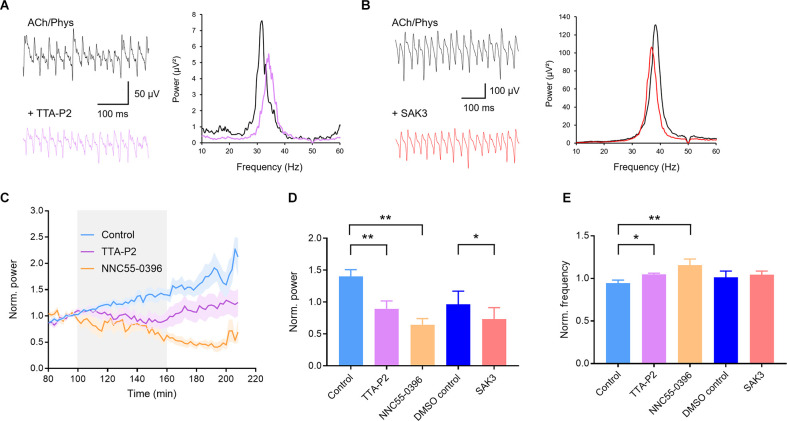
Figure 4.
Selective ligands of T-type calcium channels inhibit cholinergic gamma oscillations in rat hippocampal slices. (A) Original traces (left) and power spectra (right) of cholinergic gamma oscillations before (black) and after (purple) application of the selective T-type calcium channel blocker TTA-P2 (1 μM). (B) Original traces (left) and power spectra (right) of cholinergic gamma oscillations before (black) and after (red) application of the selective T-type calcium channel enhancer SAK3 (0.1 μM). (C) Normalized power before, during and after bath application (gray) of the selective T-type blocker TTA-P2 (1 μM, purple) and NNC55-0396 (100 μM, orange) compared to control (blue). (D) Effect of the T-type calcium channel blockers TTA-P2 and NNC55-0396 as well as the enhancer SAK3 on the power of hippocampal gamma oscillations compared to time matched and solvent control. Control (light blue): n = 13 slices, N = 9 animals; TTA-P2 (1 μM, purple): n = 14, N = 6, p = 0.005, NNC55-0396 (100 μM, orange): n = 6, N = 2, p = 0.001; DMSO control (dark blue): n = 8, N = 7; SAK3 (0.1 μM, red): n = 10, N = 6, p = 0.020. (E) Effect of the T-type calcium channel blockers TTA-P2 and NNC55-0396 as well as the enhancer SAK3 on the peak frequency of hippocampal gamma oscillations compared to time matched and solvent control. TTA-P2 (1 μM, purple): p = 0.042; NNC55-0396 (100 μM, orange): p = 0.001; SAK3 (0.1 μM, red): p = 0.306. Recording temperature was between 34 and 36°C. Traces were lowpass filtered at 200 Hz and bandstop filtered at 50 Hz. Bars show mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. ACh, acetylcholine; Phys, physostigmine.