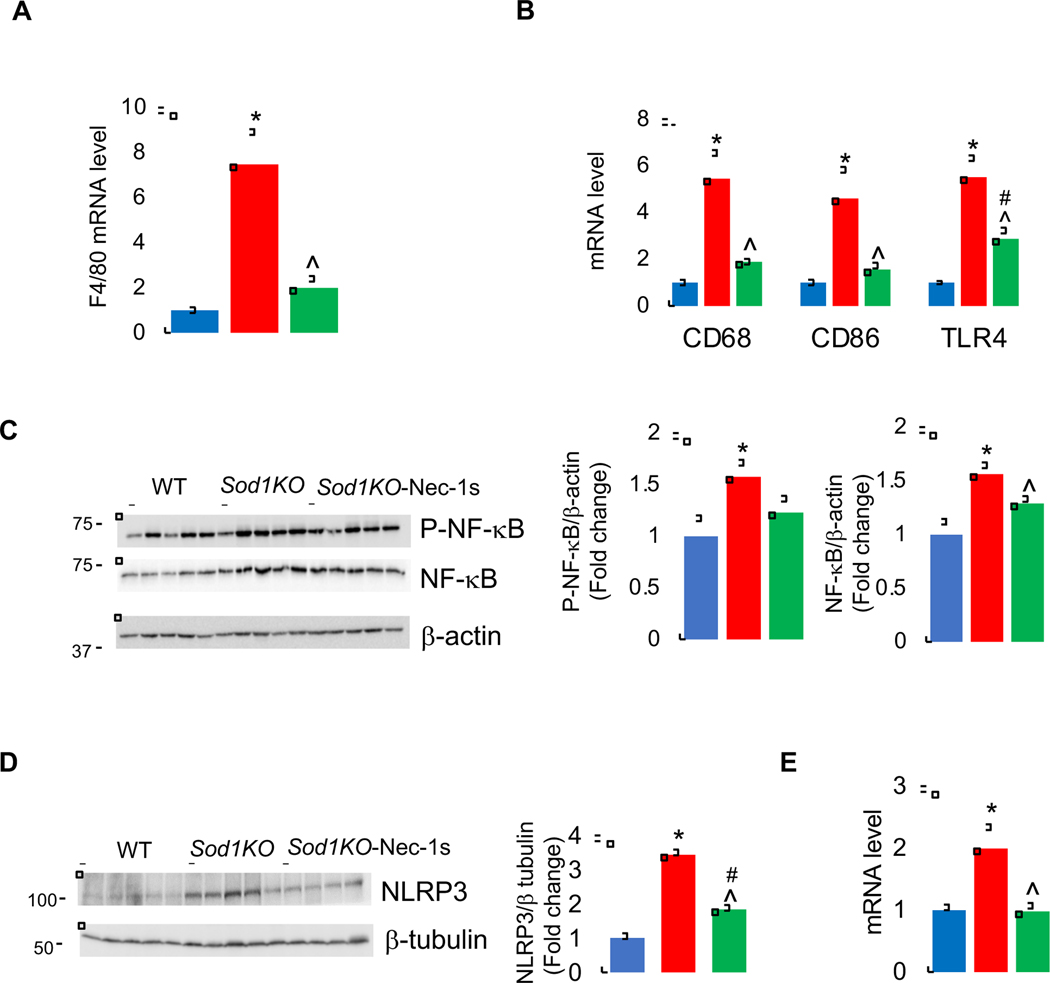
Figure 2. Effect of Sod1 deficiency and necroptosis on inflammation.
Transcript levels of F4/80 (A), and proinflammatory M1 macrophage markers CD68,CD86, and TLR4 (B) in the livers of WT (blue bars), Sod1KO untreated (red bars) and Sod1KO mice treated with Nec-1s (green bars). (C) Left panel: Immunoblots of liver extracts for phospho-NF-κB (p65), NF-κB and β-actin. Right panel: Graphical representation of quantified blots normalized to β-actin. (D) Left panel: Immunoblots of liver extracts for NLRP3 and β-tubulin. Right panel: Graphical representation of quantified blots normalized to β-tubulin. (E) Transcript levels of NLRP3. Data were obtained from 5 to 7 mice per group and are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (ANOVA, *WT-Veh vs Sod1KO-Veh; #WT-Veh vs Sod1KO-Nec-1s; ^ Sod1KO-Veh vs Sod1KO-Nec-1s; */#/^ P ≤ 0.05).