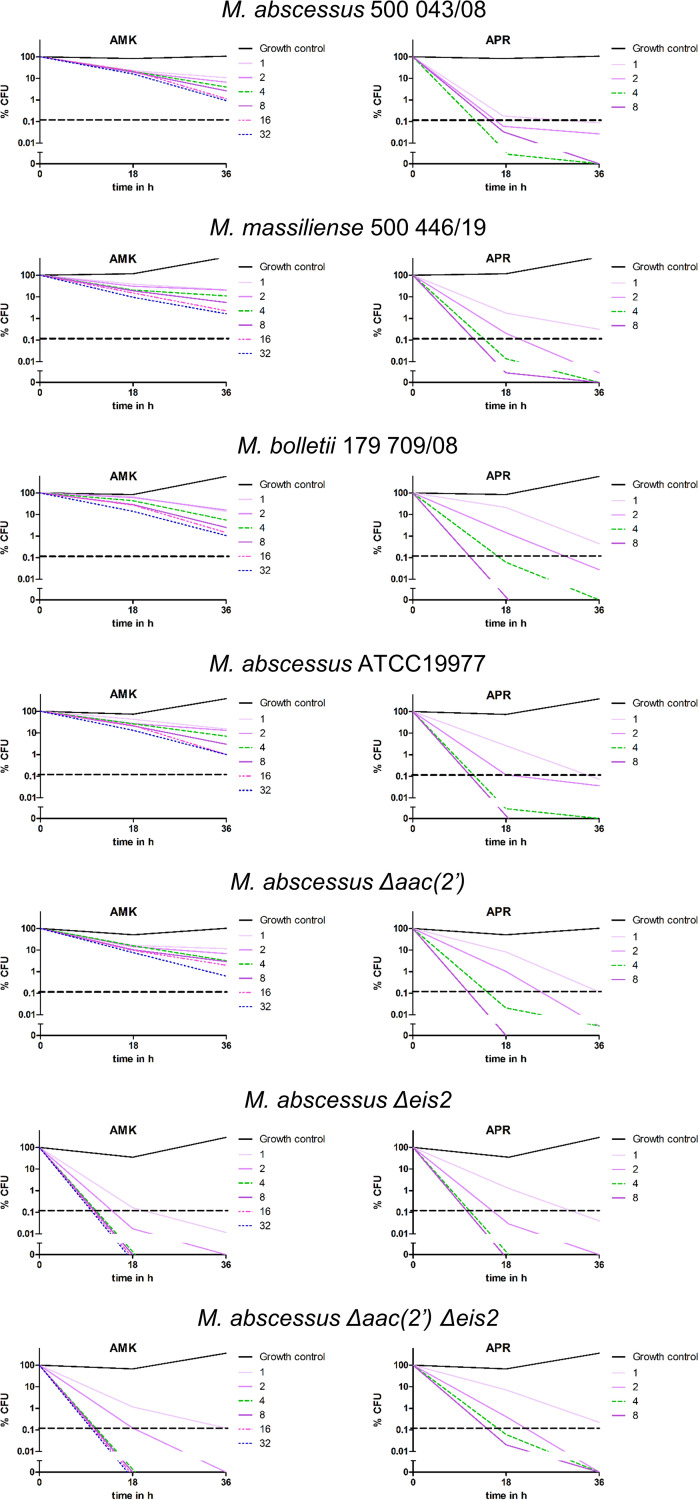
FIG 2.
Time-kill curves for amikacin and apramycin against M. abscessus strains. M. abscessus clinical isolates of the three subspecies, i.e., M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, M. abscessus subsp. massiliense, and M. abscessus subsp. bolletii, as well as M. abscessus ATCC 19977 and its genetically engineered deletion mutants M. abscessus Δeis2, M. abscessus Δaac(2′), and M. abscessus Δaac(2′) Δeis2, were exposed for 18 h or 36 h to various concentrations (0 and 0.125 to 32 mg/L) of amikacin (AMK) and apramycin (APR). Serial dilutions were spotted and incubated at 37°C for 96 h. Bacteria were counted, and the relative number of CFU, compared to time zero, was plotted. The dashed horizontal lines indicate the 99.9% killing threshold that defines bactericidal activity.