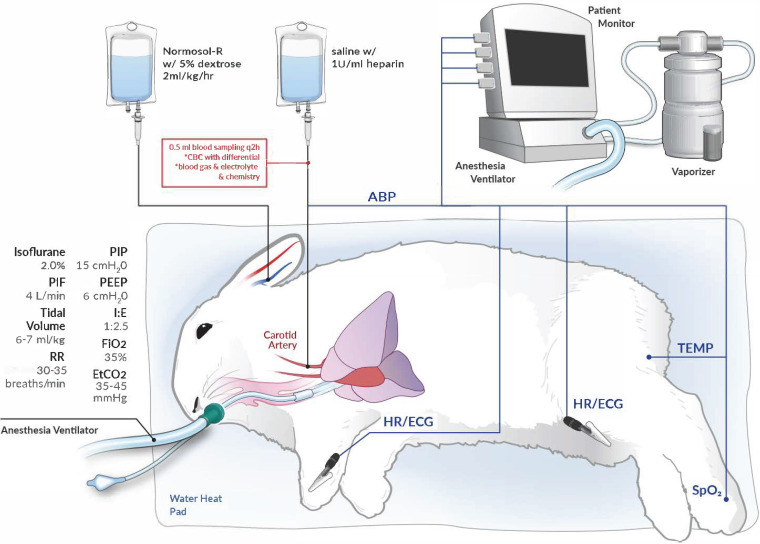
FIG 1.
Schematic of the experimental setup for a rabbit model of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Rabbits were intubated and mechanically ventilated with a PIP of 15 cm H2O, PEEP of 6 cm H2O, peak inspiratory flow (PIF) of 4 L/min, and FiO2 of 0.35, with 2.0% isoflurane to maintain general anesthesia. The respiratory rate (RR) was adjusted to 30 to 35 breaths/min to achieve end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) of 35 to 45 mm Hg. The mechanical ventilation parameters resulted in a low tidal volume of 6 to 7 mL/kg and an inspiratory/expiratory ratio (I:E) of 1:2.5. The carotid artery was cannulated for serial blood sampling and arterial blood pressure (ABP) monitoring. The marginal ear vein was cannulated for infusion of Normosol-R with 5% dextrose for fluid maintenance. The patient monitor was used for continuous monitoring of heart rate (HR), electrocardiogram (ECG), rectal temperature, and peripheral capillary oxygen saturation (SpO2).