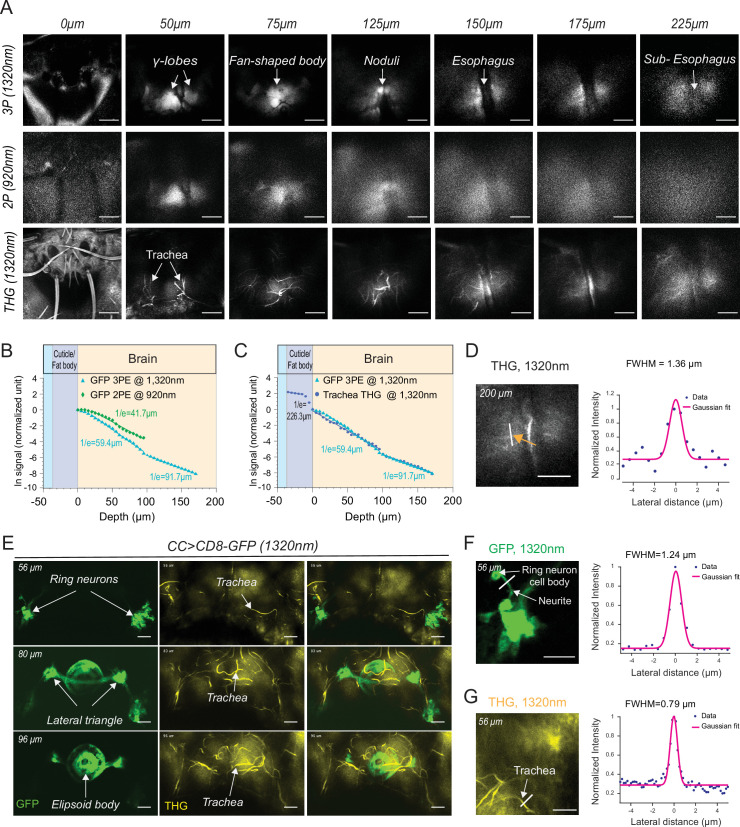
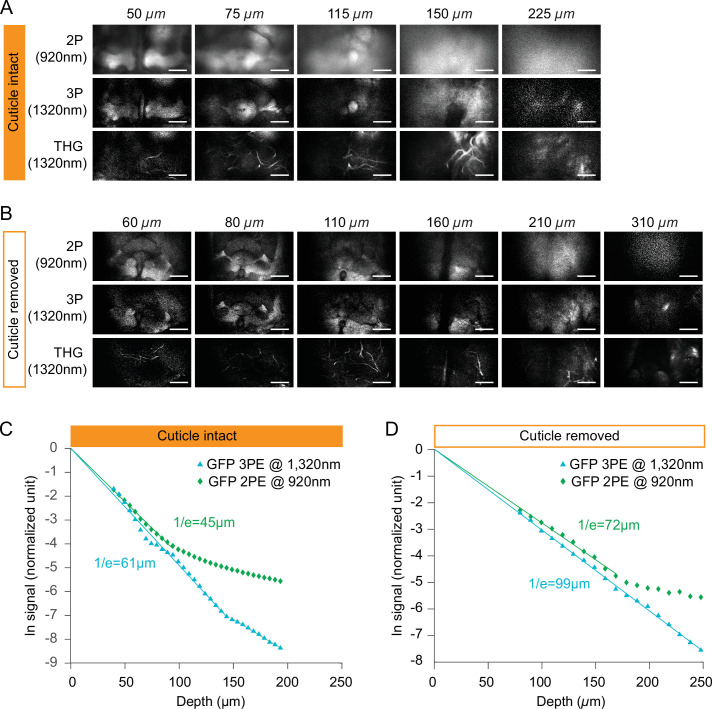
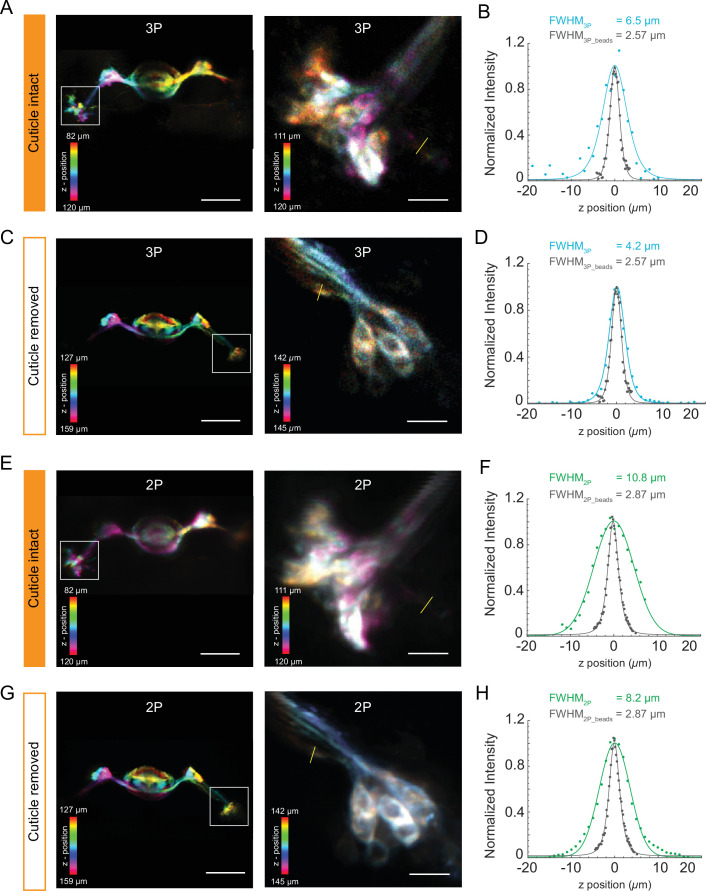
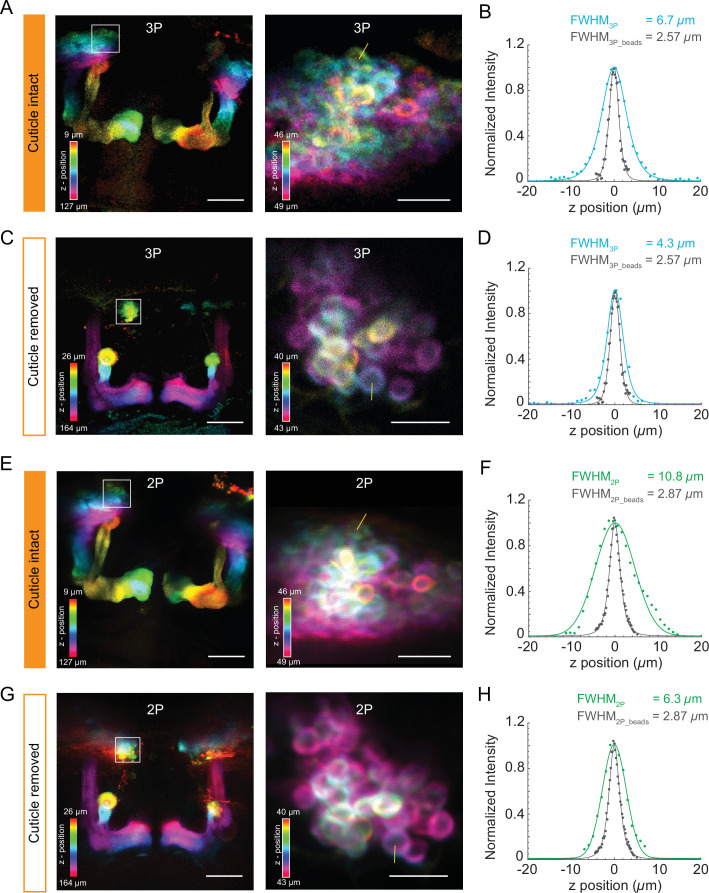
Figure 3. 2P and 3P structural imaging of the fly brain.
(A) Cross-section images of the fly brain through the cuticle with 3P (top) and 2P (bottom) excitation at different depths. The third harmonic generation (THG) images are included at the bottom. 3P excitation power is <11 mW and the repetition rate is 333 kHz. 2P excitation power is <15 mW and the repetition rate is 80 MHz, scale bars = 50 µm. (B) GFP signal as a function of depth for 920 nm 2P excitation and 1320 nm 3P excitation. (C) Comparison of the GFP signal and THG signal as a function of depth at 1320 nm. (D) Lateral resolution measurement in the THG image captured at 200 µm depth. Lateral intensity profile measured along the white line (indicated by the orange arrow) is fitted by a Gaussian profile for the lateral resolution estimation (scale bar = 50 µm). (E) Cross-section images of the central complex (CC) ring neurons through the cuticle with 1320 nm 3P excitation (green). THG imaging visualizes the tracheal arbors (yellow). Arrows indicate different CC compartments that are identified (scale bars = 30 µm). (F–G) Lateral resolution measurements in 3P images captured at 56 µm depth. (F) The GFP fluorescence profile of CC ring neurons (green) and (G) the THG profile of surrounding trachea (yellow). Lateral intensity profiles measured along the white lines are fitted by Gaussian profiles for the lateral resolution estimation (scale bars = 20 µm).