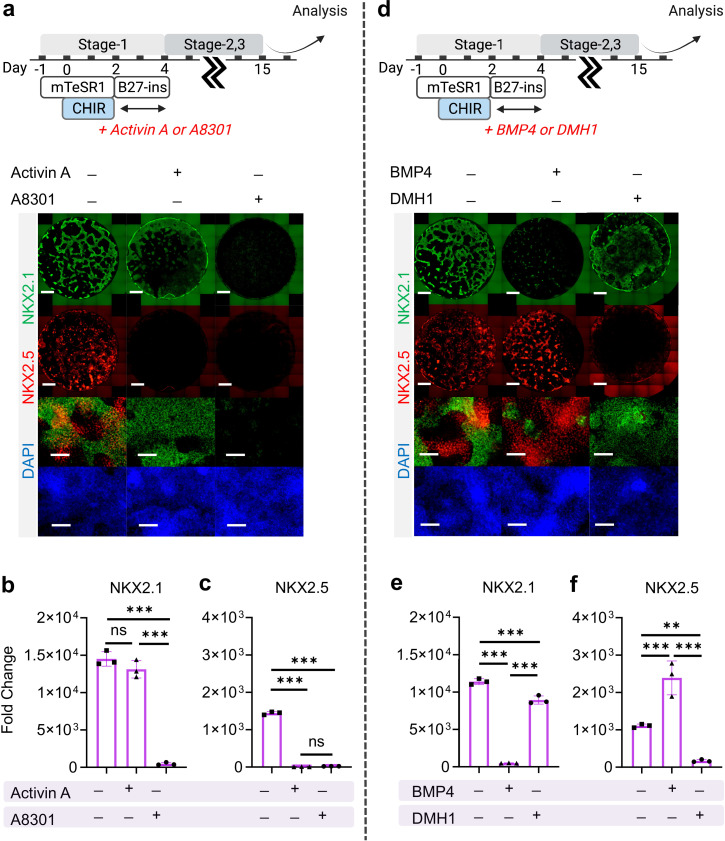
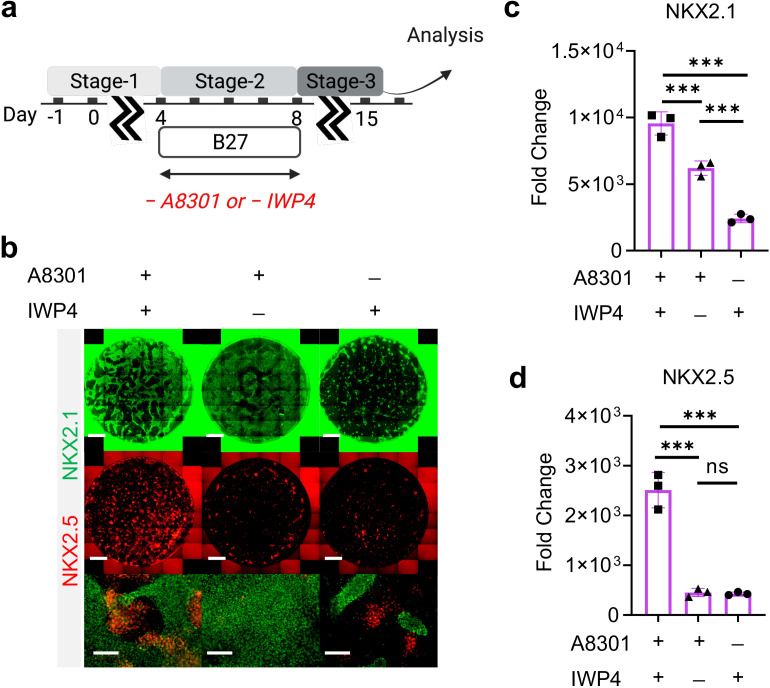
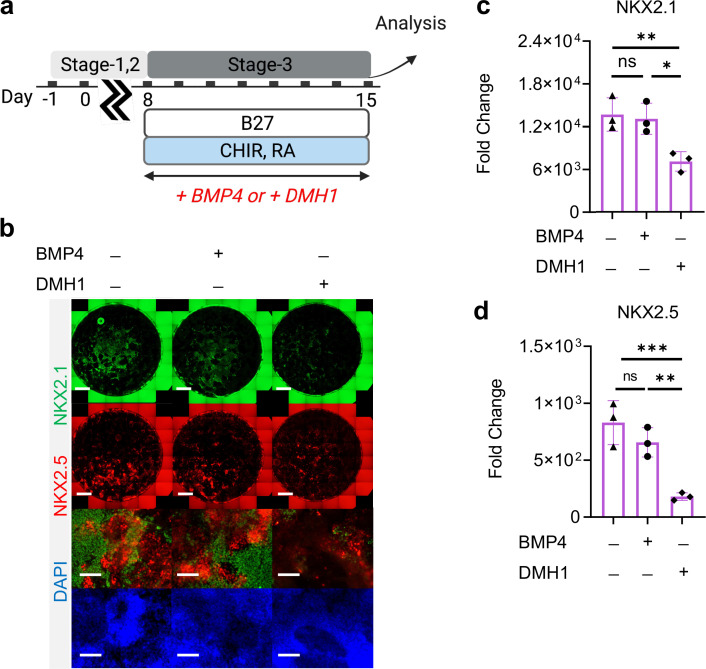
Figure 3. The effect of Nodal and BMP signaling during Stage-1 of co-differentiation on cardio-pulmonary induction.
IF (a,d) and qPCR (b,c,e,f) analysis of the induction of lung (NKX2.1+) and cardiac (NKX2.5+) progenitors on Day-15 of differentiation (a–c) The effects of exogenous nodal activation (Activin A, 20 ng/mL) or its inhibition (A8301, 1 µM). Fold change over hiPSCs for (b) NKX2.1 (n = 3 each; Activin A─ /A8301─ vs. Activin A+ /A8301─, p = 0.1939; Activin A─ /A8301─ vs. Activin A─ /A8301+, p < 0.001; Activin A+ /A8301─ vs. Activin A─ /A8301+, p < 0.001) and (c) NKX2.5 (n = 3 each; Activin A─ /A8301─ vs. Activin A+ /A8301─, p < 0.001; Activin A─ /A8301─ vs. Activin A─ /A8301+, p < 0.001; Activin A+ /A8301─ vs. Activin A─ /A8301+, p = 0.8649). (d-f) The effects of exogenous BMP4 (20 ng/mL) or BMP inhibitor (DMH1, 2 µM). qPCR analysis of (e) NKX2.1 (n = 3 each; BMP4─ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4+ /DMH1─, p < 0.001; BMP4─ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4─ /DMH1+, p < 0.001; BMP4+ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4─ /DMH1+, p < 0.001) and (f) NKX2.5 (n = 3 each; BMP4─ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4+ /DMH1─, p < 0.001; BMP4─ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4─ /DMH1+, p = 0.0044; BMP4+ /DMH1─ vs. BMP4─ /DMH1+, p < 0.001). Scale bar = 500 μm for whole well scan; Scale bar = 125 μm for 20 X images. All data are mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. ‘n’ refers to biological replicates. Diagram created using BioRender (http://biorender.com/).