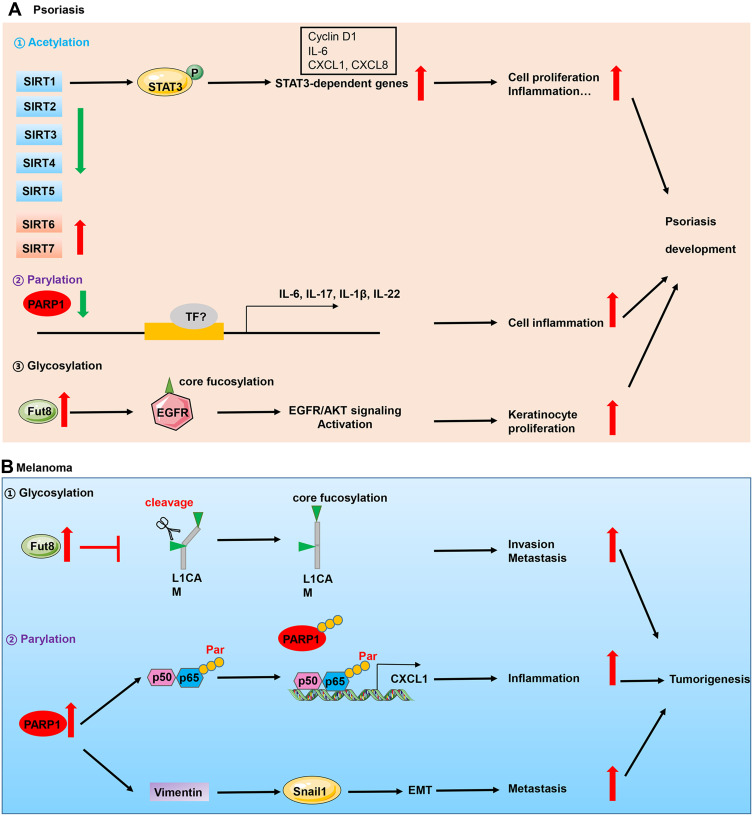
Figure 2.
Implication of PTMs in skin diseases. (A) Perturbations of acetylation, parylation and glycosylation are implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis which is an inflammatory skin disease. In the epidermis of psoriasis patients, decreased expression of PARP1 and deacetylase SIRT1, and higher expression of glycosyltransferase Fut8 contributed to keratinocyte hyperproliferation and inflammation, which triggered psoriasis development. (B) In skin cancers which is represented by melanoma, upregulation of Fut8 and PARP1 contributed to cell invasion, inflammation and metastasis.
Abbreviations: P, phosphorylation; TF, transcription factors; Par, parylation.