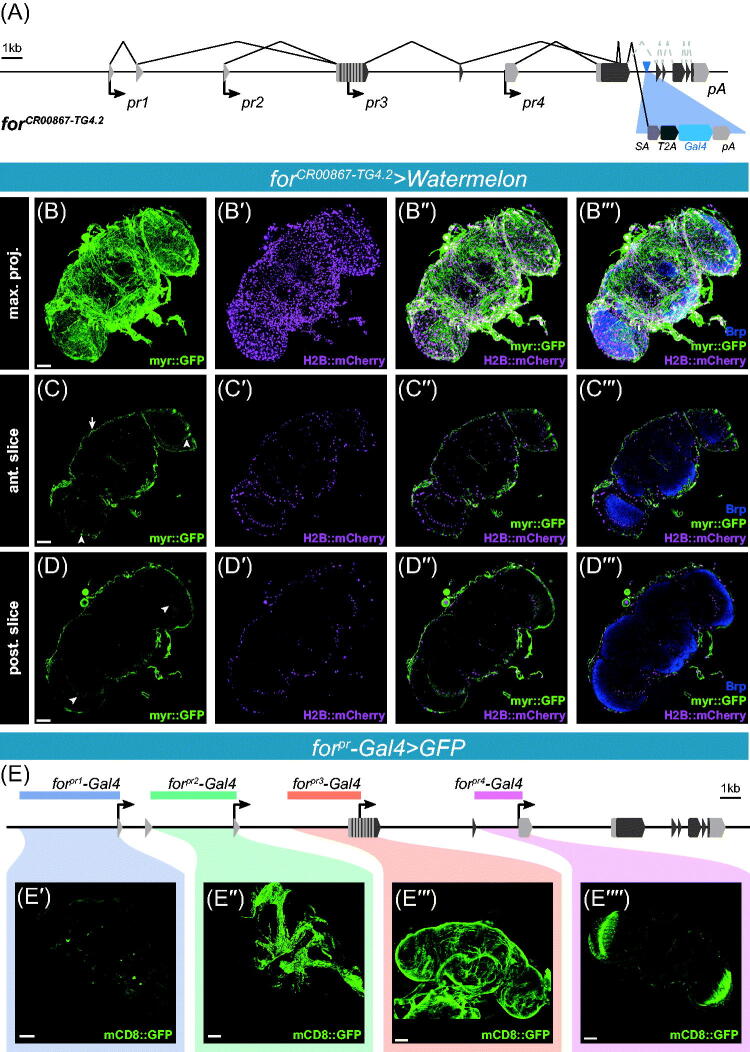
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic of the forCR00867-TG4.2 CRIMIC allele in the foraging locus. UTR regions are depicted with grey boxes and coding sequences are depicted with black boxes. Splicing patterns are depicted above the locus. The four transcription start sites are depicted below the locus, pr1–4. The CRIMIC element is inserted in the first intron after the first common coding exon (blue triangle). The splice acceptor sequence (SA) is designed to trap the endogenous transcription of foraging. The self-cleaving T2A sequence then allows for the translation of the Gal4 coding sequence into a separate peptide. (pA – poly adenylation site). (B–B′′′) Maximal projections of the forCR00867-TG4.2 CRIMIC allele driving UAS-Watermelon in the adult brain. Membrane bound GFP in green (B), nuclear mCherry in magenta (B′), membrane and nuclear merged (B′′), membrane and nuclear merged with Bruchpilot (nc82) in blue (B′′′). (C–C′′′) A single section in the anterior of the adult brain of the forCR00867-TG4.2 CRIMIC allele driving UAS-Watermelon. Arrow denotes surface glia expression. Arrow heads in the optic lobes depict the cells with morphology consistent with outer chiasm glia. (D–D′′′) A single section in the posterior of the adult brain of the forCR00867-TG4.2 CRIMIC allele driving UAS-Watermelon. Arrowheads in the optic lobes depict the cells with morphology consistent with inner chiasm glia. (E–E′′′′) Schematic of the foraging locus depicting regions of cloned forpr-Gal4s (E). forpr1-Gal4 driven GFP expression in neurons innervating the optic lobe (E′). forpr2-Gal4 driven expression in the trachea and air sacs (E′′). forpr3-Gal4 driven expression in the perineurial surface glia (E′′′). forpr4-Gal4 driven expression in the outer optic chiasm glia (E′′′′). Scale bars = 50 µm. [Please refer to the online version for colors.]