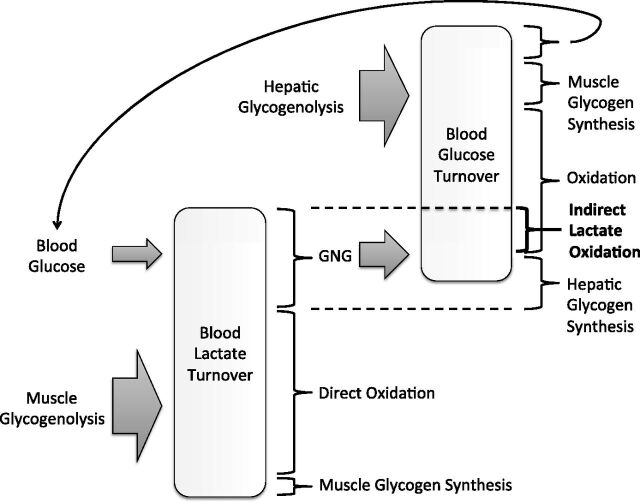
Fig. 4.
A schematic showing the relationship between lactate and glucose turnover in the blood. Muscle glycogenolysis is the primary source of lactate appearance, followed by glycolysis of blood glucose. Lactate disposal includes direct oxidation, gluconeogenesis (GNG), and to a lesser extent, glycogen synthesis. Glucose appearance is dependent on hepatic glycogenolysis and GNG, and glucose disposal includes oxidation and glycogen synthesis. A small portion of glucose disposal also re-enters the lactate pool. Indirect lactate oxidation is the portion of lactate that undergoes conversion to glucose via GNG and subsequent oxidation.