Figure 1. Schematic of protein splicing and the H. walsbyi cdc21 precursor.
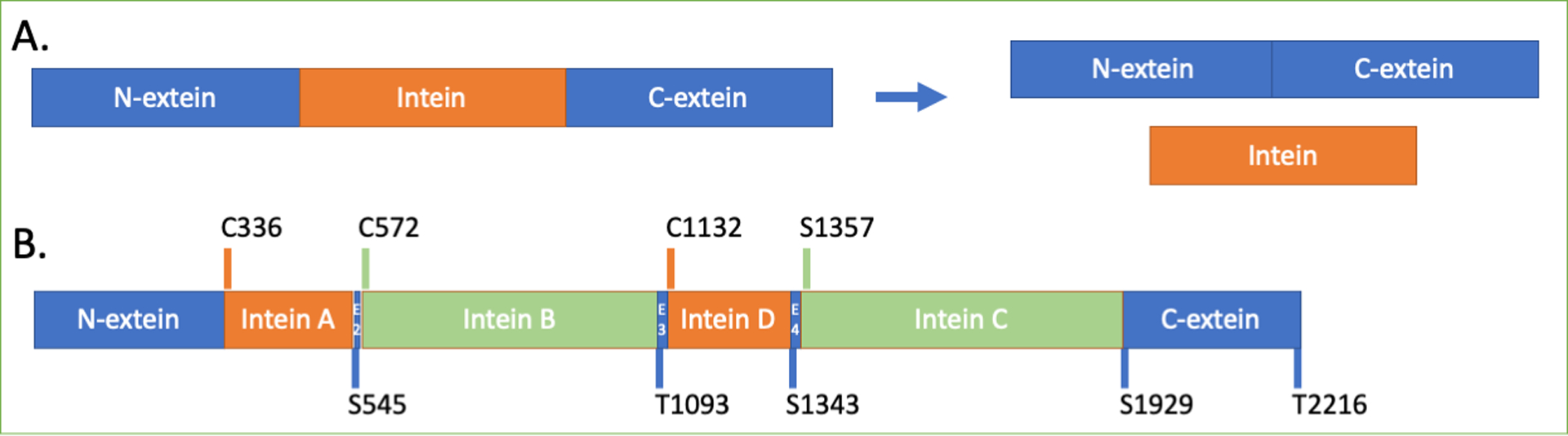
A. Protein splicing results in the excision of an intein from flanking polypeptides (the N- and C-exteins) concomitant to extein ligation to produce a functional extein protein. B. The insertion sites of the four inteins that interrupt the cdc21 protein in H. walsbyi. Mini-inteins (A and D) are in orange, and homing endonuclease-containing inteins are in blue (B and C). The codes above the schematic indicate the amino acid residue that is the first residue of the intein (orange or green bar), and those below indicate the first residue of the extein segment (blue). The insertion sites were named in the order of their discovery and are therefore out of alphabetical order, and the schematic is approximately to scale.
