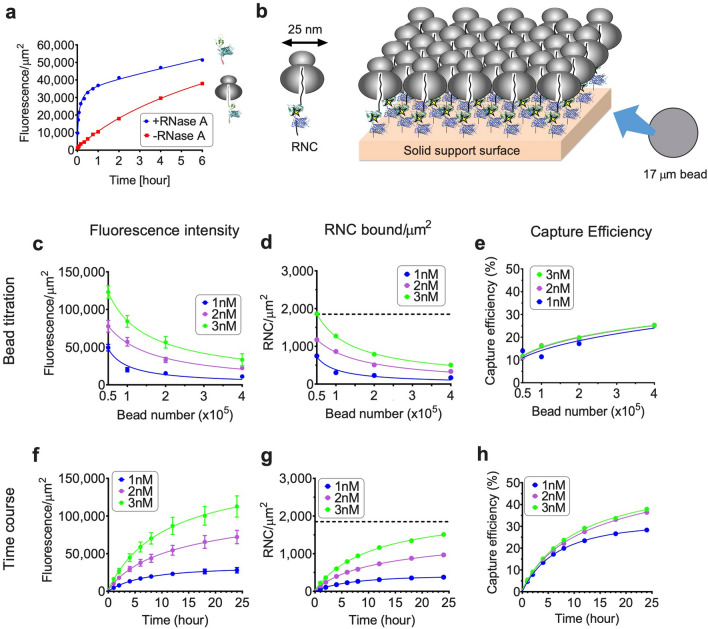
Figure 2.
RNC capture is dependent on RNC concentration, binding time, and bead number. (a) Time course of bead binding for 2 × 105 of 17 µm beads and 2 nM purified RNCs (His10-CFP-NBD1, donor only) ± RNase A treatment. (b) Cartoon depicting ribosome binding geometry on solid support surface assuming smooth surface. Diameter of ribosome is approximately 25 nm, yielding RNC saturation density of: h(1 µm)2/(r2) = 1,850 ribosomes/µm2, where h is the coefficient of densest packing of circle in the plane, and r is radius of ribosome. (c–e) Effect of bead number on RNC binding. 1, 2, or 3 nM RNCs (His10-CFP-NBD1, donor only) were incubated with 0.5–4 × 105 of 17 µm beads for 6 h. (f–h) Effect of incubation time on RNC binding. 1, 2, or 3 nM RNCs (His10-CFP-NBD1 donor only) incubated with 2 × 105 of 17 µm beads for times indicated. Fluorescence intensity of 17 µm beads in panels c and f are shown in mean ± SD (n = ~ 400 beads). Binding density in panels d and g was calculated using number of protein molecules bound per total calculated surface area of beads added. Dotted line in panels d and g indicates theoretical RNC saturation density as described in panel b. Capture efficiency in panels e and h was calculated by RNCs bound/RNCs in binding reaction.