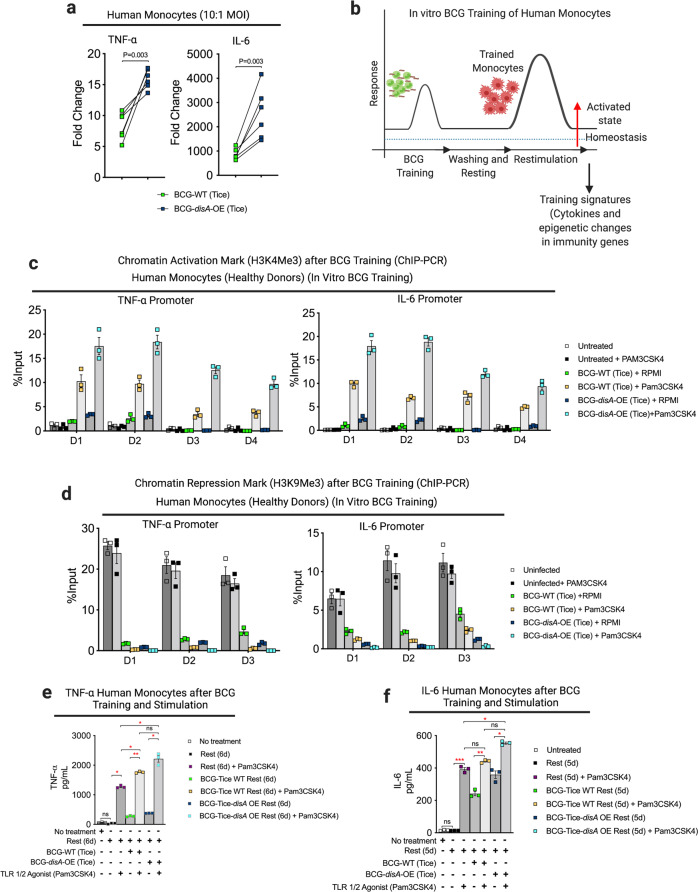
Fig. 3. Compared with BCG-WT, BCG-disA-OE is a more potent inducer of epigenetic changes characteristic of trained immunity in primary human monocytes.
a mRNA levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in primary human monocytes (n = 6 healthy donors) relative to RNU6A after 24 h exposures at a MOI of 10:1. Statistical analysis done using multiple unpaired t-test with Bonferroni-Dunn method. b Schematic diagram of in vitro monocyte training. c Relative levels of the H3K4me3 chromatin activation mark (n = 4 healthy donors; D1–D4) or d the H3K9me3 chromatin repression mark retrieved from TNF-α and IL-6 promoter regions of primary human monocytes from 3 (n = 3) health donors (D1–D3) determined by ChIP-PCR assay on day 6. e, f Secreted cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) following BCG training and re-stimulation. Monocytes were initially challenged on day 0 with a 24 h exposure to the BCG strains at a MOI of 10:1 followed by washing. After 5 days of rest, they were treated for 24 h with either a sham stimulus (RPMI) or the TLR1/2 agonist Pam3CSK4 (n = 3 healthy donors). Data are presented as mean values ± S.E.M. Statistical analyses done using two-tailed Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).