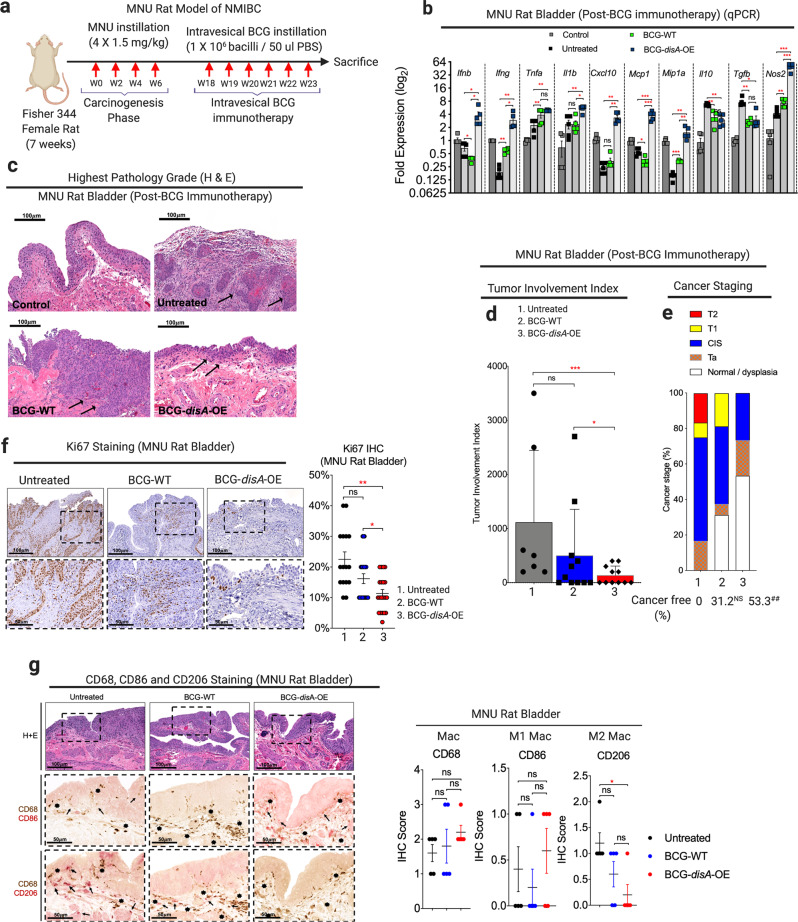
Fig. 5. BCG-disA-OE elicits improved antitumor efficacy over BCG-WT in the orthotopic carcinogen-induced rat model of urothelial cancer.
a Schematic diagram of the MNU rat model of NMIBC. b mRNA levels for pro-inflammatory cytokines (Ifnb, Ifng, Tnfa, and Il1b), regulatory chemokines (Cxcl10, Mcp1, and Mip1a), immunosuppressive M2-like macrophage cytokines (Il10 and Tgfb) and M1-like tumoricidal effectors (Nos2) in whole bladders at necropsy (wk 23) measured by qRT-PCR relative to GAPDH (n = 5 animals/group). c Representative H&E staining showing highest pathology grade for each group [control, untreated MNU bladder, BCG-WT (Past and Tice), and BCG-disA-OE (Past and Tice) (n = 12–16 animals/group)]. d Tumor involvement values at necropsy (7–11 animals/group). e Highest tumor stage at necropsy. f Representative immunohistochemistry and bar graph of rat bladder tissue at necropsy stained for Ki67 (n = 17–22 animals). g Representative immunohistochemical co-staining and line graph for CD68 (brown), CD86 (M1-like macrophages; red) and CD206 (M2-like macrophages; red) in rat bladder tissues at necropsy (n = 5 animals per group). Data are presented as mean values ± S.E.M. (qRT-PCR) or mean values ± S.D. (tumor involvement index, Ki67 staining and IHC scores). Statistical analyses done using two-tailed Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001) (qRT-PCR) and one-way ANOVA (##P < 0.01).