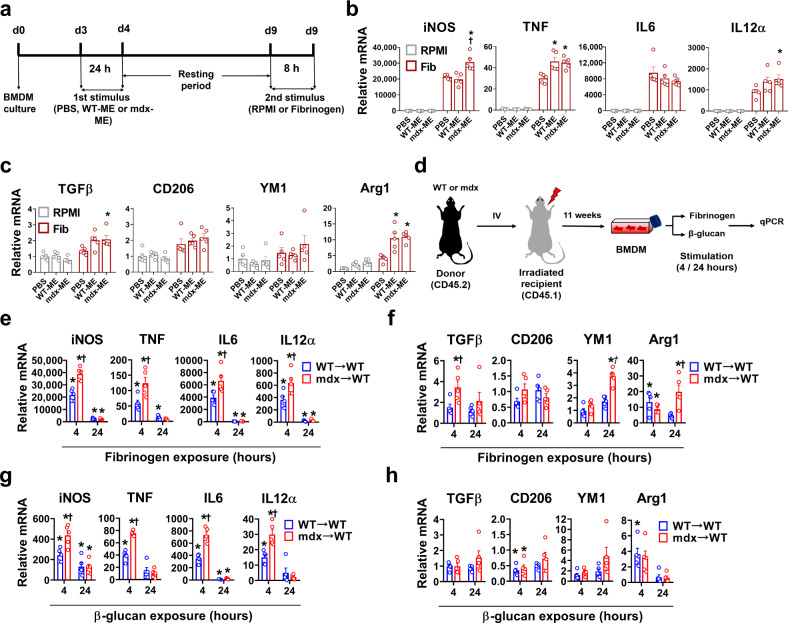
Fig. 4. BMDM exposed to muscle damage show a trained-like phenotype both in vitro and in vivo.
a Experimental design for WT- or mdx- muscle extract (ME) exposure to induce trained immunity in naive WT BMDM. b, c Transcript levels are shown for BMDM trained with PBS, WT-ME, or mdx-ME and then secondarily exposed to fibrinogen (Fib) or RPMI for 8 h; the mRNA levels determined by qPCR are expressed relative to the mean control (PBS-trained and RPMI-stimulated) value (n = 5/group). d Schematic representation of the BM transplant chimeric model. At 11 weeks post-transplantation BMDM were generated from recipient mice previously transplanted with whole BM from either WT (WT → WT) or mdx (mdx → WT) mice at necrotic phase. The BMDM were stimulated with fibrinogen or β-glucan for 4 and 24 h (e–h); e (n = 4 for TNF in 24 h mdx group, rest n = 5/group), f (n = 5/group), g (n = 4 for TNF in 4 h mdx group, rest n = 5/group), h (n = 4 for TGFβ and CD206 WT 4 h groups, rest n = 5/group). Data represent means ± SEM of biologically independent samples from different mice. b, c *P < 0.05 vs. PBS-trained and †P < 0.05 vs. WT-ME trained. e–h *P < 0.05 vs. WT-unstimulated and †P < 0.05 vs. WT-stimulated group at a given time point (one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post-hoc test, two-tailed). See Source Data file for the exact P-values.