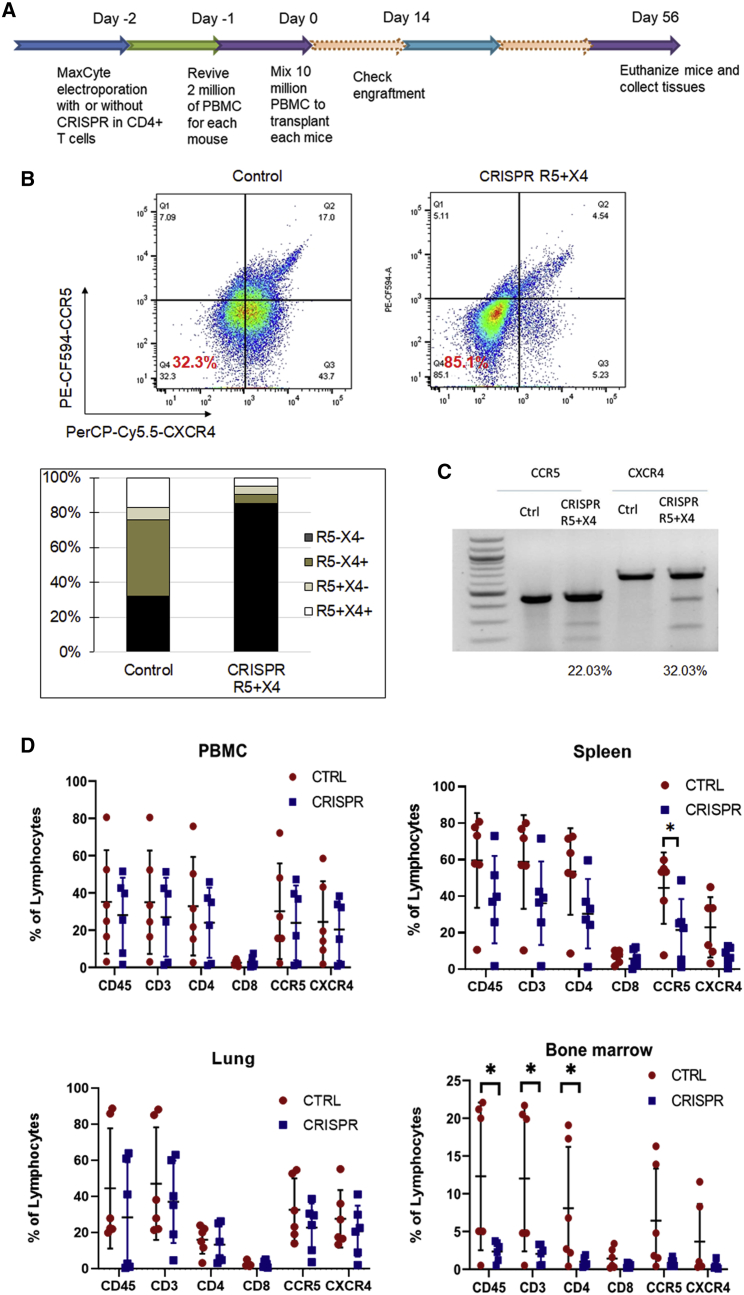
Figure 6.
Bio-distribution of CCR5- and CXCR4-CRISPR knockout CD4+ T cells in Hu-PBMC mouse tissues
(A) Schematic of the timeline of building hu-PBMC mouse model by using mixed human primary PBMCs with CXCR4 CRISPR-modified CD4+ T cells. (B) Cell surface CCR5 and CXCR4 co-receptor knockout in CD4+ T cells after MaxCyte electroporation of CCR5 and CXCR4 guide RNAs and Cas9 RNPs. Cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde and analyzed by flow cytometry 48 h after transfection. (C) Surveyor assay detection of CCR5 and CXCR4 allelic disruption in CD4+ T cells after MaxCyte electroporation of CCR5 and CXCR4 guide RNAs and Cas9 RNPs. (D) Eight million CRISPR-modified or unmodified CD4+ T cells with 2 million human PBMCs were transplanted into NSG mice. At the final time point, whole PBMCs, spleens, lungs, and bone marrow of all the mice from each group were harvested, and cells were analyzed by flow cytometer (n = 6, ∗p < 0.05).