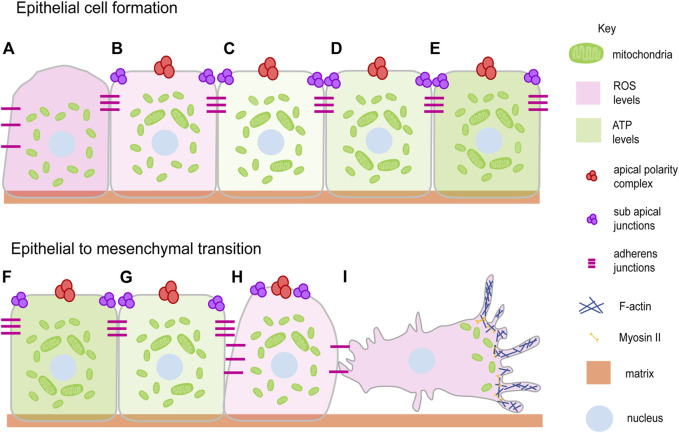
FIGURE 1.
Mitochondrial dynamics and epithelial architecture. Mitochondria transit from spherical to elongated shape during progressive epithelial cell formation and maturation (Fu et al., 2013; Dao Thi et al., 2020) (A–E). This occurs over 6–7 days when liver cell polarization is allowed to occur in vitro. Epithelial polarity is lost during epithelial to mesenchymal transition during several processes such as cell migration, wound closure and disease progression with the change in the mitochondrial shape from elongated to spherical (G–I). EMT brings the migratory ability to the cell by detaching and losing polarity complexes (Denisenko et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2019) (I). Mitochondria elongate and show an increase in ATP generating ability (light green gradient) during epithelial cell formation (B–E) and become fragmented showing a decrease in ATP generating ability during EMT (Lee et al., 2019) (F–I). The ROS levels decrease (light pink gradient) during epithelial cell formation (A–E) and increase during EMT (Zhang et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020) (F–I). Mitochondria (Green), Apical polarity complexes (Red), Sub apical junctions (Purple), Adherens junctions (Pink), Matrix (Light orange), Nucleus (Light blue).