Fig. 4. Summary of miRNAs that target fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
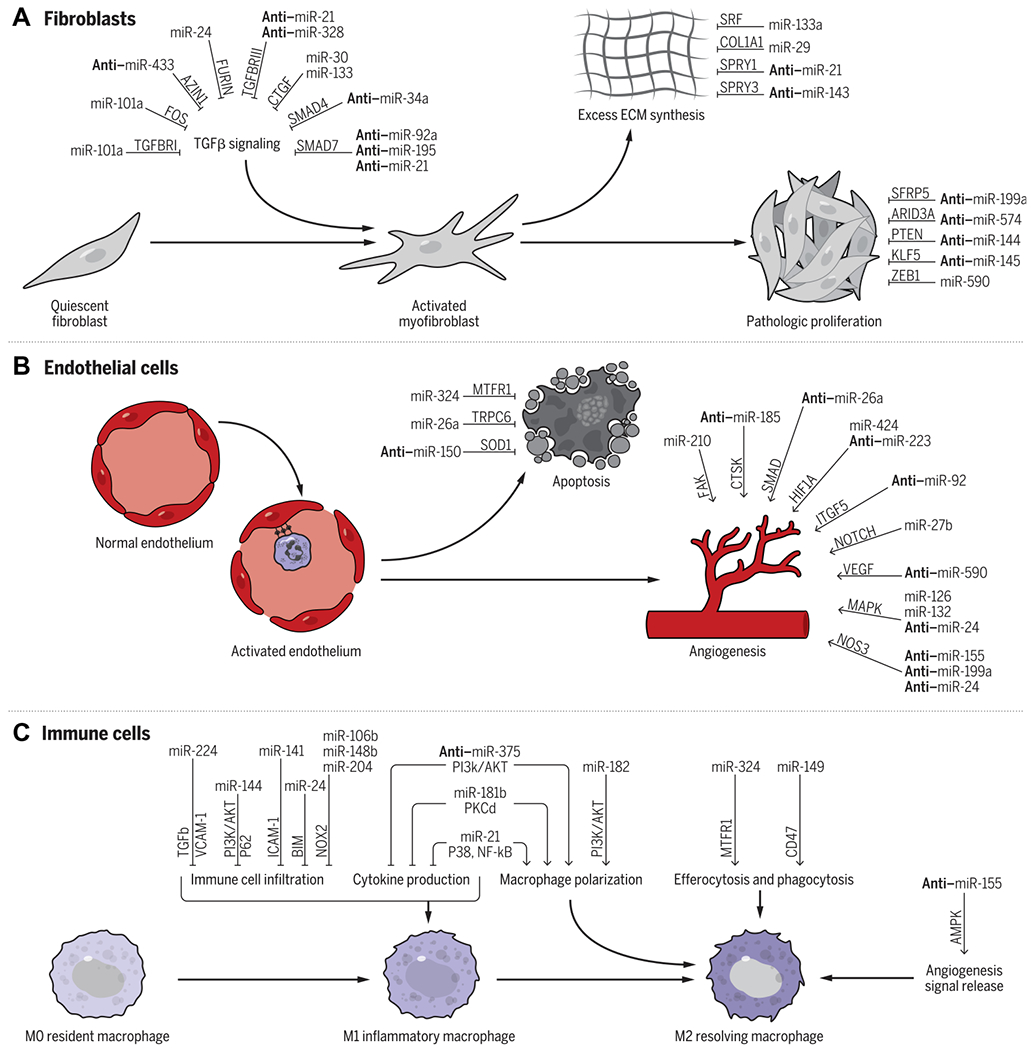
(A) In CFs, miRNAs can regulate TGFβ signaling as well as ECM synthesis and pathological proliferation. (B) In ECs, a large number of miRNAs have been shown to regulate angiogenesis, whereas others have been shown to regulate EC apoptosis. (C) In immune cells, miRNAs can regulate multiple aspects of macrophage function including immune cell infiltration, cytokine production, macrophage polarization, efferocytosis, and phagocytosis, as well as angiogenesis signal release. Select well-characterized miRNAs, their targets (written above the arrows), and the processes that they regulate are shown (i.e., miR-24 prevents TGFβ activation through FURIN signaling). miRNAs prefaced with anti–denote that the inhibition of the miRNA is therapeutic (i.e., the inhibition of miR-433 prevents TGFβ activation through AZIN1 signaling). For the complete list of miRNAs reviewed, please see table S1.
