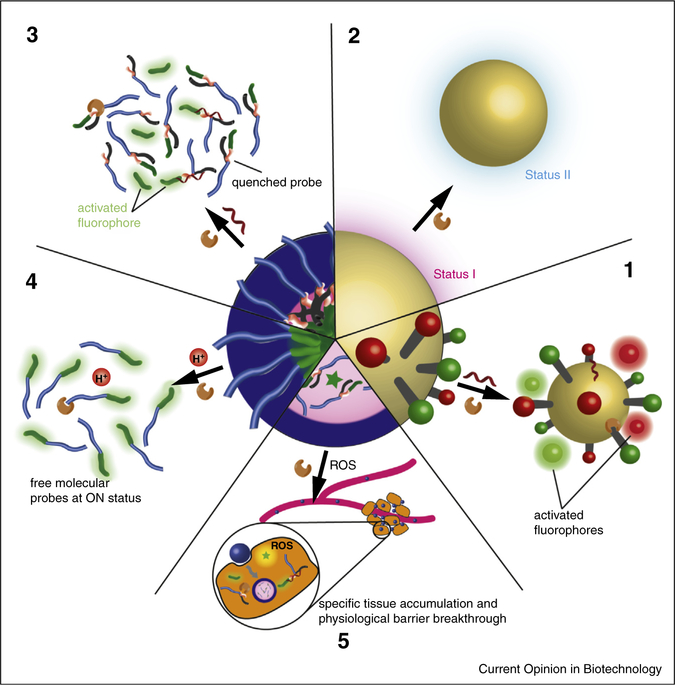
Figure 1.
Generic illustration of the unique features offered by activatable nanoprobes for probing disease-relevant biomolecules. Inorganic nanoparticles can serve as universal quenchers for simultaneous detection of multiple biomolecules (1). Switchable signals from the inorganic nanoparticle itself can also serve as an indicator for the presence and activities of biomolecules of interest (2). Self-assembly of activatable molecular probes (3) or always-ON probes (4) can improve their chemical and structural stability, and also offer an additional activation mechanism. The use of additional nanoparticles as carriers could improve the accumulation of molecular probe in target tissues (5).