Figure 6: Anisotropic mechanical properties of the matrix relate to mechanosensing cellular behavior.
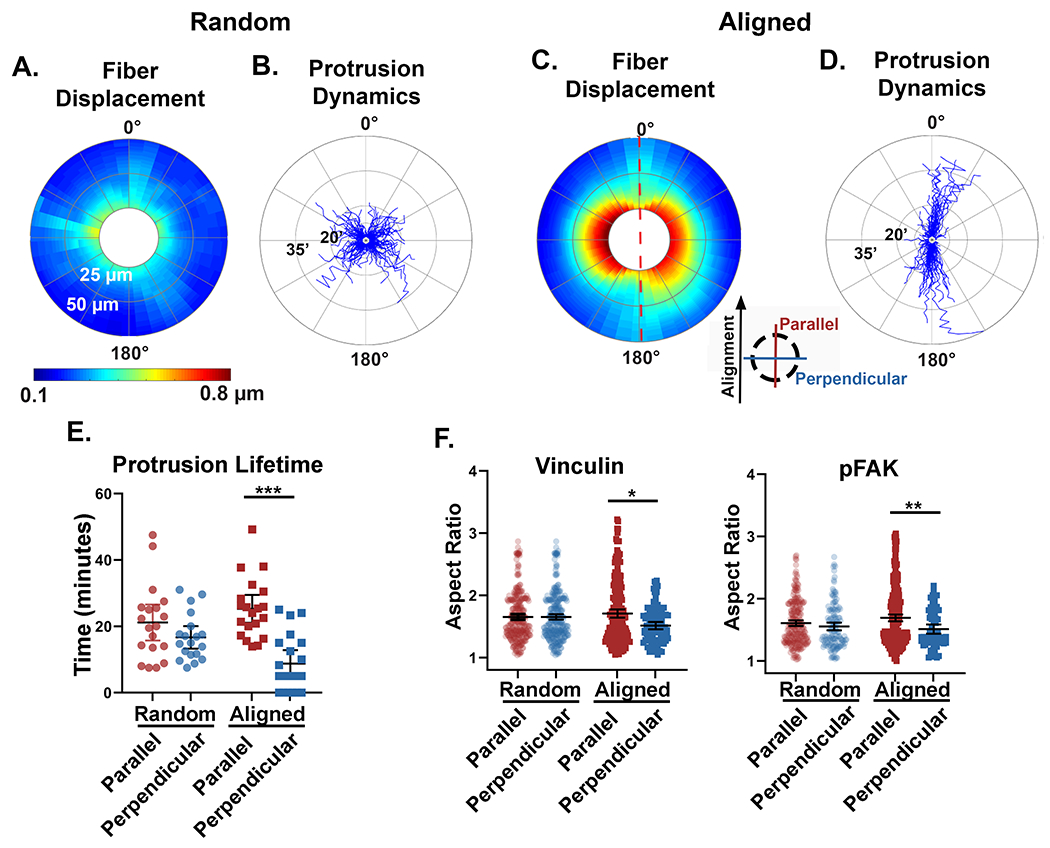
A and C) Fiber displacements were circumferentially extracted from the perimeter of multiple cells and plotted on 360° polar plots. The color scale represents the average magnitude of fiber displacements relative to the cell perimeter (n=10 cells for each fiber architecture). Fiber displacements were quantified out to 50 μm from the cell perimeter (radial axis). The red dashed line in panel C represent the axis of collagen alignment and the inserted key denotes the orientation of parallel and perpendicular directions with respect to the fiber alignment. B and D) Windrose plots described the dynamic and spatial protrusive behavior of individual cells in random (n=19 cells, 1,058 protrusions) and aligned (n=20 cells, 741 protrusions) matrices. The protrusion lifetime was measured in minutes on the radial axis. E) Quantification of the average parallel and perpendicular protrusion lifetimes per cell for random (n=19 cells) and aligned (n=20 cells) fiber architectures. Protrusions that were identified in only one timepoint were quantified as zero lifetime. F) Quantification of the aspect ratio of pFAK and vinculin positive focal adhesions oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the axis of fiber alignment. Medians and interquartile ranges were reported, and significance was determined by Mann-Whitney. (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001)
