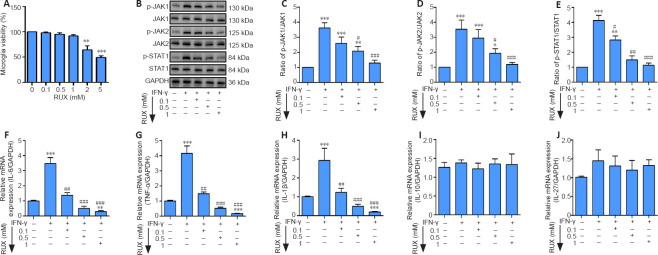
Figure 1.
RUX mitigates IFN-γ-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines in microglia by targeting the JAK/STAT1 axis.
Microglia were treated with 0.1, 0.5, or 1 mM RUX for 24 hours, followed by stimulation with IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) for 6 hours. (A) Cell viability of microglia as determined by cell counting kit-8 assay (n = 4 in each group). (B) Western blot of p-JAK1, JAK1, p-JAK2, JAK2, p-STAT1, and STAT1 expression in microglia. (C–E) Quantitation of p-JAK1/JAK1 (C), p-JAK2/JAK2 (D), and p-STAT1/STAT1 (E) ratios in the in vitro experiments. (F–J) mRNA expression levels for IL-6 (F), IL-1β (G), TNF-α (H), IL-10 (I), and IL-27 (J) in microglia as determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (n = 5 in each group). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The experiments were repeated four (A) and five (B–J) times; the results shown in C–J were normalized to the Con group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. 0 mM/Con group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, vs. IFN-γ group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc test). GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IFN-γ: interferon-γ; IL: interleukin; JAK: Janus kinase; p-JAK: phosphorylated Janus kinase; p-STAT1: phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; RUX: ruxolitinib; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.