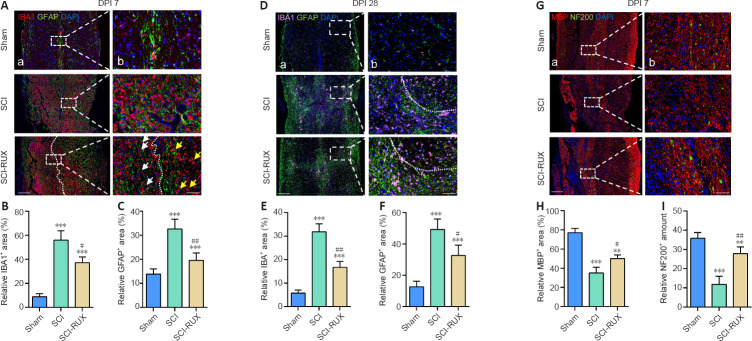
Figure 4.
RUX ameliorates inflammation-induced neuropathology in SCI mice.
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images of IBA1+ (red, Alexa Fluor 594)/GFAP+ (green, Alexa Fluor 488) cells in the injured spinal cord at 7 days post-SCI (DPI). The white arrows indicate activated microglia, which have an amoeba-like shape; the yellow arrows indicate the resting branching microglia. The white dashed line separates the relatively proximal and distal injury foci. SCI caused widespread and scattered microglial activation and astrocyte assembly, but treatment with RUX confined the activated microglia to a region proximal to the lesion and reduced the accumulation of astrocytes. (B, C) Quantification of microglia (B) and astrocytes (C) at 7 days post-SCI. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images of IBA1+ (pink, Alexa Fluor 647)/GFAP+ (green, Alexa Fluor 488) cells in the injured spinal cord at day 28 post-SCI. The white dashed line separates tight and loose areas of the glial scar: the area below the line was proximal to lesion, and the area above the line was distal to the lesion. SCI caused widespread and scattered glial scar, but treatment with RUX compacted the glial scar structure closer toward the injury focus. (E, F) Quantification of microglia (E) and astrocytes (F) at 28 days post-SCI. (G) Representative immunofluorescence images of NF200+ (green, Alexa Fluor 488)/MBP+ (red, Alexa Fluor 594) cells in the injured spinal cord at 7 days post-SCI. SCI caused excess loss of myelin and neurofilaments compared with the sham mice, but treatment with RUX partly protected against these effects compared with the SCI mice. Scale bars: 200 μm in A, and 50 μm in B. (H, I) Quantification of myelin (H) and axons (I) in the injured spinal cord at 7 days post-SCI. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5 per group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, vs. SCI group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc test). GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; IBA1: ionized calcium binding adaptor 1; MBP: myelin basic protein; NF200: neurofilament 200; RUX: ruxolitinib; SCI: spinal cord injury.