Figure 3.
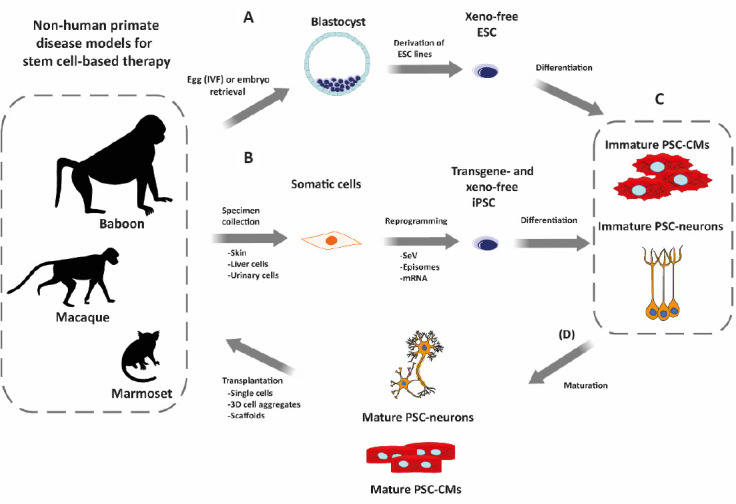
Overview of the workflow for testing pluripotent stem cells (PSC)-based regeneration therapies in non-human primates (NHP).
(A) Embryonic stem cell (ESC) are derived from naturally or artificially fertilized embryos. (B) Alternatively, induced PSC (iPSC) are generated from NHP somatic cells obtained by biopsy (invasive) or non-invasively from, e.g., urinary tract cells present in urine. Non-integrative reprogramming methods (RNA-based like Sendai virus (SeV) or mRNA; DNA-based like episomes) are used to deliver the reprogramming factors. During ESC derivation and iPSC reprogramming, cells are maintained under xeno-free conditions. (C) Upon NHP-PSC generation and characterization, the PSC can be differentiated into tissue-specific cell types, e.g., cardiomyocytes (PSC-CMs) or neurons (PSC-neurons). PSC-derived cells, however, present mostly immature, fetal-like phenotypes. (D) Before transplantation, different approaches can be employed to mature the differentiated cells. The differentiated cell types can be used directly for transplantation or after aggregation to tissues in 3D molds/scaffolds. PSC-derived cells are then transplanted back into the NHP model of choice following allogeneic or autologous approaches. CM: Cardiomyocytes.
