Figure 1.
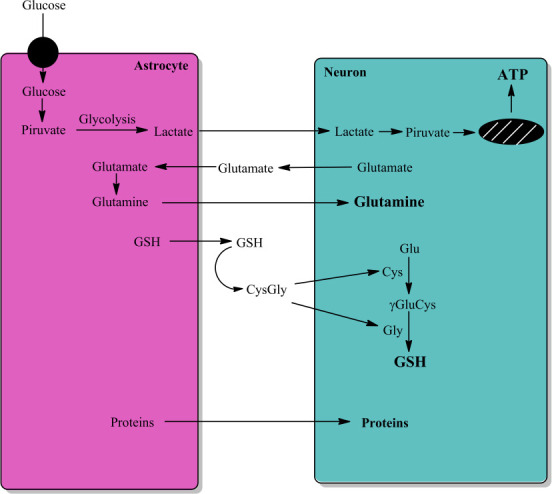
Astrocyte-neuron interactions.
The interaction between astrocytes and neurons is very important for neuron function and survival. Astrocytes convert glucose to lactate that it is transported to neuron with aim to generate energy (ATP). Astrocyte take up glutamate released by neurons to convert it to glutamine by astrocytic expressed glutamine synthetase, and neurons take up glutamine. Astrocytes secrete GSH that it is converted to Cys-Gly, which is converted to cysteine and glycine. Neurons take up both cysteine and glycine that are used in the synthesis of GSH. Astrocytes also secret a large number of proteins, including GSTM2, that neurons take up. Unpublished data. ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; Cys: L-cysteine; CysGly: L-cysteinyl-glycine; GSH: reduced tripeptide composed of L-glutamine, L-cysteine, and glycine; γGluCys: gamma-glutamyl-cysteine.
