Figure 4.
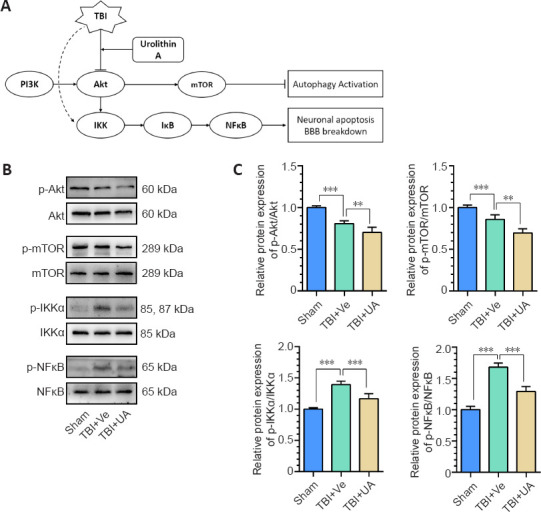
PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Akt/IKK/NFκB signaling pathways may be involved in the neuroprotective effect of urolithin A.
(A) Pattern diagram of involved pathways. UA downregulates Akt phosphorylation, thus reinforcing autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and alleviates inflammation via the Akt/IKK/NFκB signaling pathway. (B) Representative western blots of p-Akt, Akt, p-mTOR, mTOR, p-IKKα, IKKα, p-NFκB, and NFκB. (C) Quantification of relative protein expression (n = 5). Data are represented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test). Akt: Protein kinase B; BBB: blood-brain barrier; BBB: blood-brain barrier; IKK: inhibitor of NFκB kinase; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; NFκB: nuclear factor kappa B; p-Akt: phospho-Akt; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; p-IKKα: phospho-IKKα; p-mTOR: phospho-mTOR; p-NFκB: phospho-NFκB; TBI: traumatic brain injury; TBI: traumatic brain injury; UA: urolithin A; Ve: vehicle.
