Figure 1.
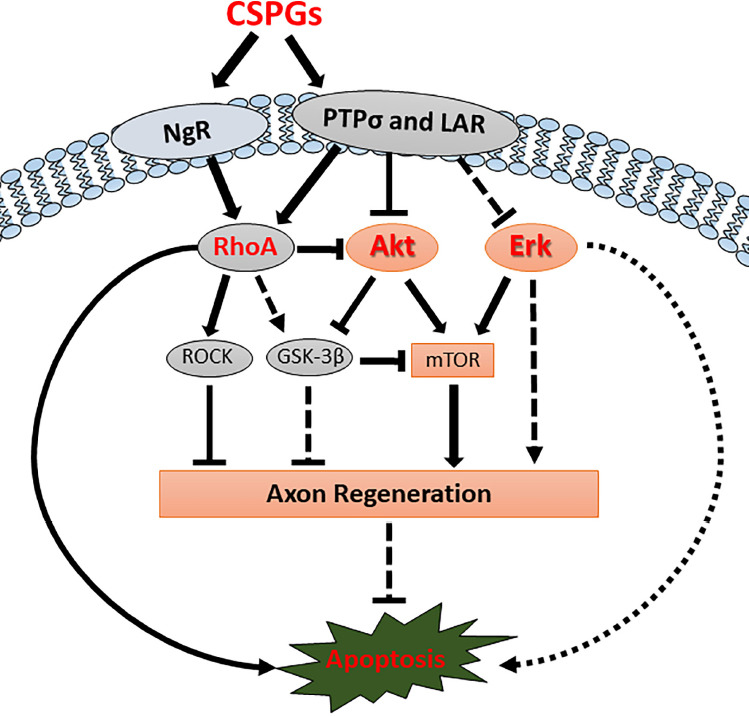
In vivo downstream signaling pathways of CSPGs and CSPG receptors.
CSPGs inhibit axon regeneration and induce retrograde apoptosis by binding CSPG receptors (PTPσ, LAR and NgRs) and affecting their downstream signaling pathways. CSPG receptors activate RhoA and inactivate Akt signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting axon regeneration and inducing retrograde neuronal apoptosis. Chondroitinase ABC treatment can remove the binding of CSPGs from CSPG receptors and re-activate the Akt signaling pathway after SCI, thus promoting axon regeneration and reducing retrograde neuronal apoptotic signaling. Erk activity has been reported to be modulated by CSPG receptors in vitro, but the specific in vivoroles after SCI are still unclear. CSPG: Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans; Erk: extracellular regulated kinase; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3β; LAR: leukocyte common antigen-related phosphatase; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; NgR: Nogo receptor; PTPσ: protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma; ROCK: Rho-associated kinase; SCI: spinal cord injury.
