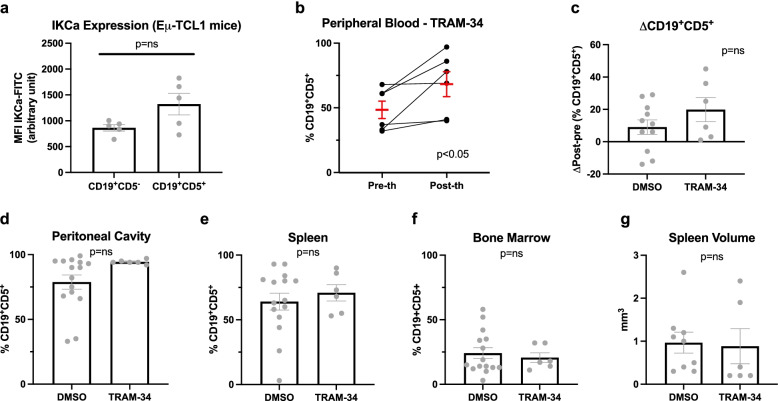
Fig. 5.
IKCa inhibition does not induce CLL cell death in Eμ-TCL1 mice. a IKCa expression in CD19+CD5− and CD19+CD5+ cells from peripheral blood of Eμ-TCL1 mice was assessed by flow cytometry. IKCa expression is reported as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI, arbitrary units). Data were obtained from 5 independent experiments and are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance of differences was assessed with the Mann–Whitney test. b-c Percentage of CD19+CD5+ cells was assessed by flow cytometry on ex vivo peripheral blood cells from Eμ-TCL1 mice before and after i.p administration of DMSO or 10 nmol/g TRAM-34 (b). Data were obtained from 15 independent experiments with DMSO and 6 with TRAM-34. As the quantity of DMSO injected with PAPTP or with TRAM-34 was the same, data from all mice that received DMSO are pooled (n = 15, shown in Fig. 2d). Statistical significance of differences was assessed with the Wilcoxon test. c Differences between the post- and pre-treatment percentages of CD19+CD5+ cells are reported for the experiments shown in b. Statistical significance of differences was assessed with the Mann–Whitney test. d-g Percentages of CD19+CD5+ cells were assessed by flow cytometry on ex vivo cells from peritoneal cavity (d), spleen (e), and bone marrow (f) of Eμ-TCL1 mice before and after i.p. administration of DMSO or TRAM-34. Statistical significance of differences was assessed with the Mann–Whitney test. g Spleen volume of the mice reported above was measured by hydrostatic weighing. Statistical significance of differences was assessed with the Mann–Whitney test