FIG 3.
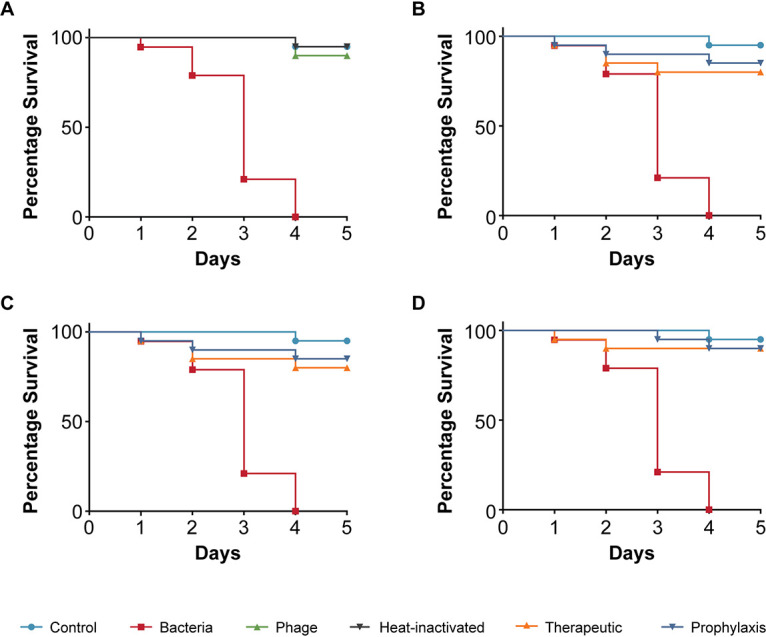
Pathogenicity of Escherichia coli strain 311 in C. elegans and efficacy of Escherichia phage myPSH2311 against E. coli infections. The control group consisted of C. elegans feed with E. coli OP50 and E. coli strain 311 (OD600 = 0.6) that kills C. elegans in liquid medium. Twenty nematodes were used in each group. Representative survival curves of C. elegans following infection by E. coli strain 311 in (A) liquid medium consisting of M9 buffer and E. coli culture, Escherichia phage, heat-inactivated bacteria and (B, C, D) survival curves of C. elegans following infection with E. coli strain 311 and treatment with Escherichia phage, therapeutic and prophylactic treatment. (B) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with bacteria and phage ratio of 1:1, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 105 PFU/mL. (C) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with bacteria and phage ratio of 1:10, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 106 PFU/mL. (D) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with bacteria and phage ratio of 1:100, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 107 PFU/mL. The survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the log-rank test was used to analyze the difference in survival rates in GraphPad Prism 7.0. A statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) was observed in the treatment groups.
