FIG 6.
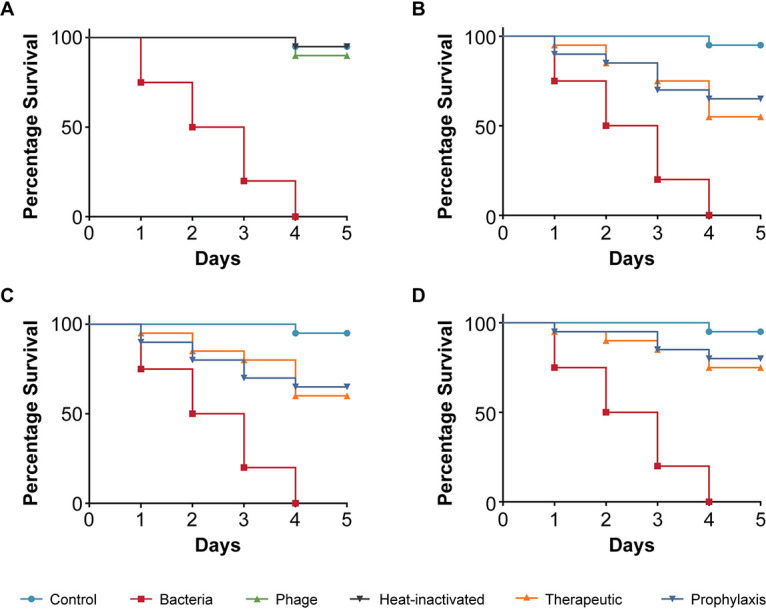
Pathogenicity of multibacterial culture in C. elegans and efficacy of phage cocktails against poly-microbial infections. The control group consisted of C. elegans fed with E. coli OP50. Twenty nematodes were used in each group. Poly-microbial culture (E. coli 131, E. coli 311, K. pneumoniae 235, E. cloacae 140) kills C. elegans in liquid medium. Representative survival curves of C. elegans following infection by poly-microbial culture in (A) liquid medium consisting of M9 buffer and bacterial culture or phage cocktail or head-inactivated bacteria and (B, C, D) survival curves of C. elegans following infection with poly-microbial bacteria and treatment with phage cocktail, therapeutic and prophylactic treatment. (B) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with poly-microbial bacteria and phage cocktail ratio of 1:1, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 105 PFU/mL. (C) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with poly-microbial bacteria and phage cocktail ratio of 1:10, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 106 PFU/mL. (D) Survival curves of C. elegans infected and treated with poly-microbial bacteria and phage cocktail ratio of 1:100, i.e., 105 CFU/mL and 107 PFU/mL. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the log-rank test was used to analyze the difference in survival rates in GraphPad Prism 7.0. A statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) was observed in the treatment groups.
