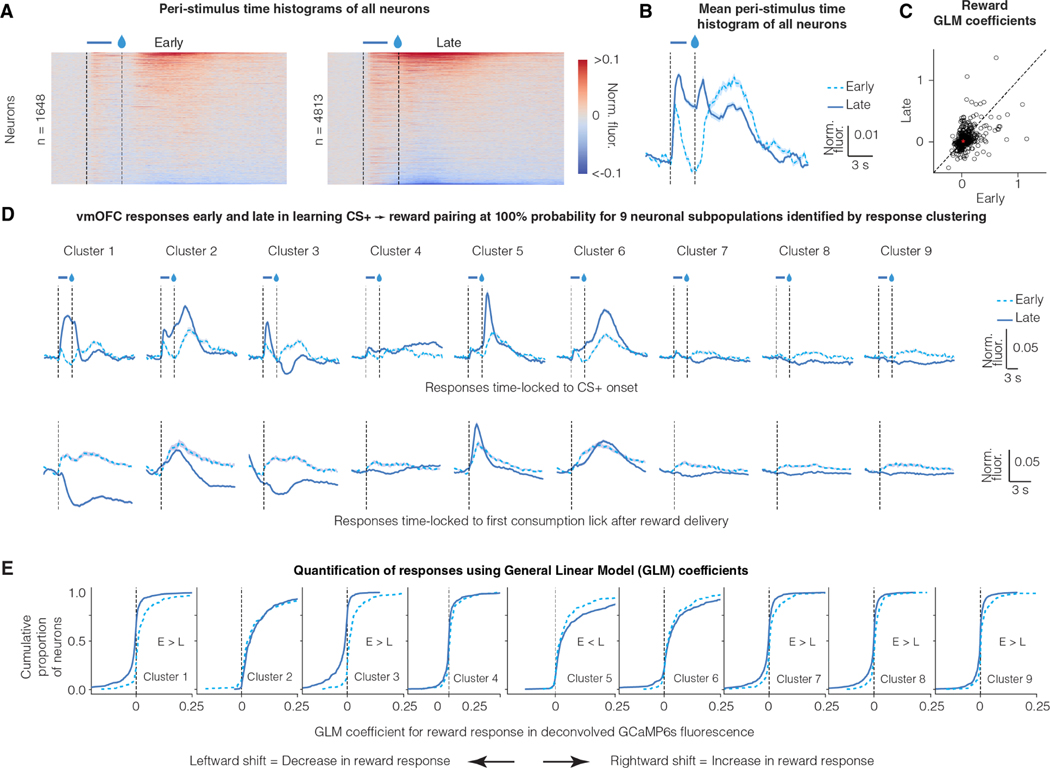
Figure 3: Reward responses of some vmOFC neuronal subpopulations reduce after reward prediction learning.
A. Peri-Stimulus Time Histograms (PSTHs) of GCaMP6s fluorescence early and late in learning for all vmOFC neurons expressing CaMKIIα (excitatory neurons). All recorded neurons from both timepoints are shown.
B. Average PSTH across all recorded neurons early and late in learning
C. General Linear Model (GLM) coefficients for reward response early and late in learning from those neurons that were longitudinally tracked between these sessions (Materials and Methods) 26 (n = 1,590 tracked neurons). We performed the GLM analyses on deconvolved fluorescence traces to remove lick response confounds and the slow decay of GCaMP6s dynamics 26. The dashed line is the identity line where responses early and late are equal. The average response early and late is indicated by the red asterisk. On an average, the neuronal response to reward reduces significantly after reward prediction learning.
D. PSTHs of GCaMP6s fluorescence early and late in learning for nine subpopulations identified using a clustering of late responses 26. Each line corresponds to the average of CS+ PSTH across all neurons within a cluster (see text for rationale). The identification of neuronal subpopulations within CaMKIIα expressing vmOFC neurons using clustering algorithms, and the PSTHs late in learning, were published previously 26. The top row shows responses time locked to cue onset and the bottom row shows responses time locked to reward consumption. Clusters 1 and 3 reverse the sign of their reward responses from positive (i.e. greater than baseline) early in learning to negative (i.e. less than baseline) late in learning. Error shadings correspond to confidence intervals.
E. Cumulative distribution function for General Linear Model (GLM) coefficients for reward response early and late in learning (Materials and Methods) 26. The y-axis effectively percentiles the responses shown on the x-axis. So, a reduction in reward response late in learning causes a leftward shift in the curves. These results demonstrate positive reward responses in all clusters early in learning, but negative reward responses in some clusters (1, 3, 7, 8 and 9) late in learning, showing a flip in sign.