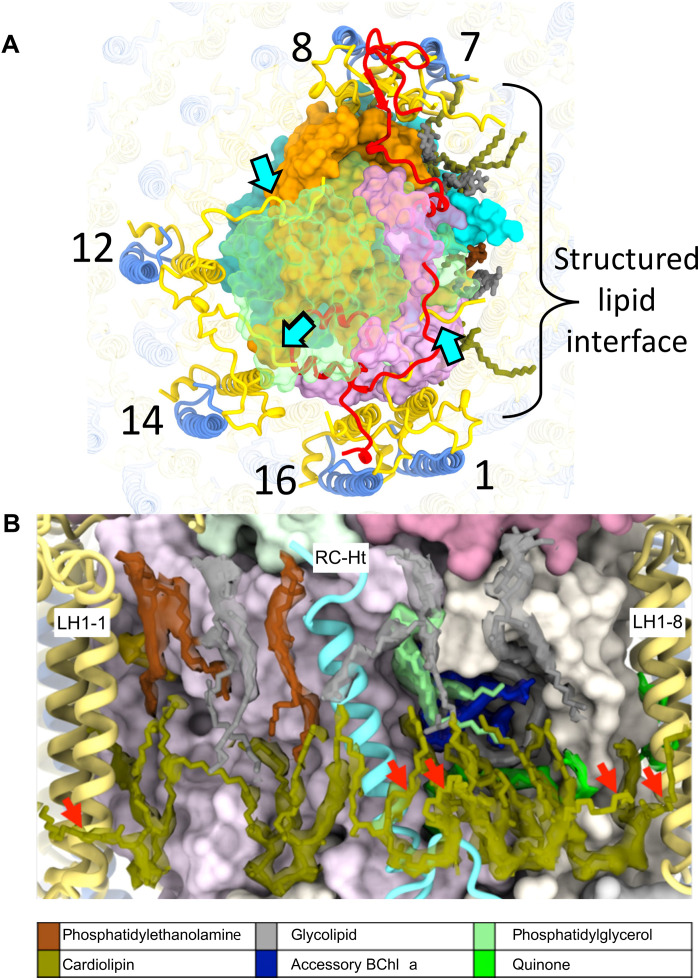
Fig. 3. Stabilization of RC-LH1 complex.
(A) View of the periplasmic face of the RC-dLH complex, showing interactions (cyan arrows) between the C termini of LH1-α1, 12, and 14 (yellow) and the RC-M and RC-C subunits (RC-C subunit is shown in translucent green). The region surrounding RC-Ht (covering the QA and spirilloxanthin sites) is dominated by a tightly packed lipid interface. On the cytoplasmic side, six cardiolipins (olive) interdigitate between RC and LH1 chains. The periplasmic interface consists of three uncharged glyceroglycolipids (gray), two phosphatidylethanolamines (brown), and a single phosphatidylglycerol (pale green). (B) View of the structured lipid interface in (A) with a 6-σ density map around the lipids. Outward-projecting cardiolipin tails are marked with red arrows.