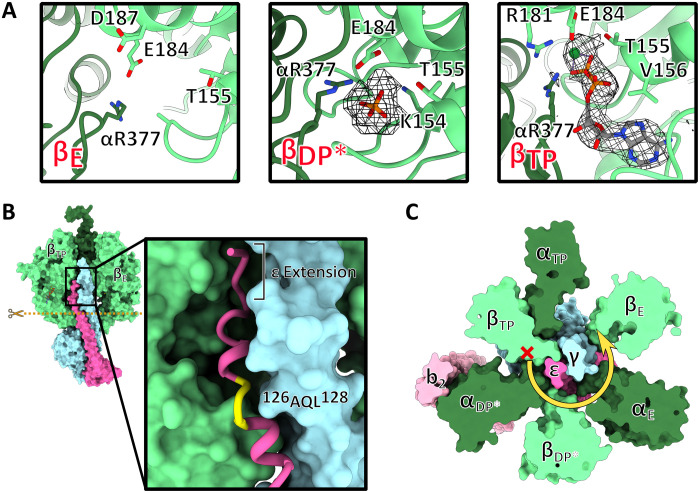
Fig. 2. Structural details in the F1 complex.
(A) Close-up views of the catalytic nucleotide binding sites in the β-subunits in cartoon representation. The maps for the nucleotide and phosphate are shown in mesh. (B) Structure of the F1 complex in surface representation including the central stalk; subunits αDP, βDP*, and αE removed to reveal how subunits γ and ε insert into the head. Inset: Close-up of the C-terminal extension of ε-subunit inserting between βTP and αDP* (not shown) showing the unwound turn of ε 126AQL128 (yellow) and the A. baumannii–specific C-terminal extension of ε. (C) Horizontal section of F1 as indicated by the dashed line in (B) reveals mechanism of unidirectional inhibition. Steric clashes between ε and βTP prevent rotation of the central stalk in the ATP hydrolysis direction (red cross) but permit unlocking and rotation in the ATP synthesis direction (yellow arrow).