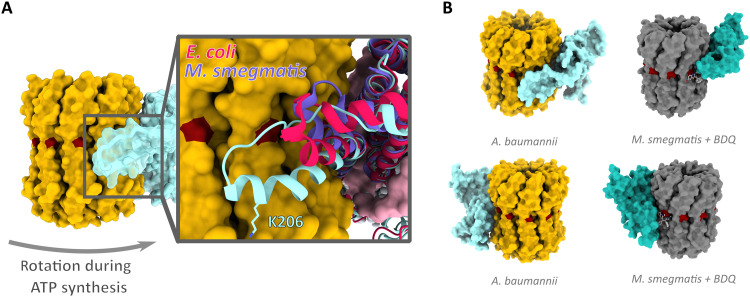
Fig. 4. Acinetobacter-specific a-subunit extension at the proton exit channel.
(A) Surface representation of c-ring (yellow) and a-subunit (translucent cyan) viewed from within the membrane plane. Inset: Structural alignment of a-subunits from A. baumannii and E. coli (PDB: 6OQR) (39) and M. smegmatis (PDB: 7JGA) (16) indicates extent of a-subunit loop insertion. K206 shown in stick representation. (B) Comparison of a/c10 interface in A. baumannii (yellow and light blue) and in M. smegmatis [dark gray and turquoise, PDB: 7JGA (16)] showing the binding site of BDQ in M. smegmatis (light gray ball and sticks); proton-carrying residues are shown in dark red. Bottom panels are rotated by 180° around the membrane normal.