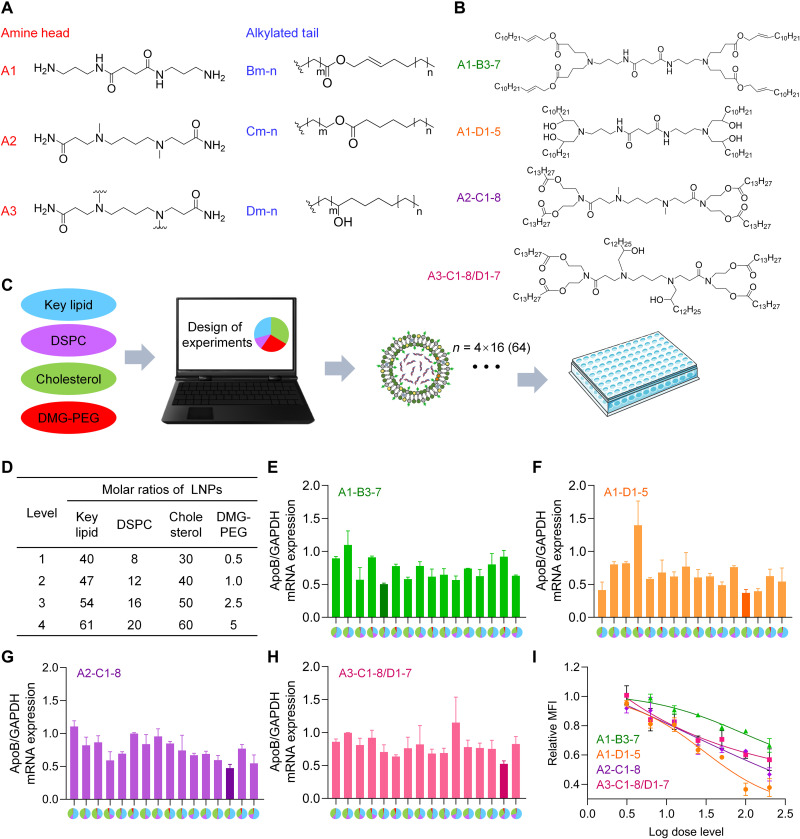
Fig. 1. Screening and component optimization of novel iLNPs.
(A) The chemical structures of lipid building blocks, including three amine heads and three alkylated tails. (B) Chemical structures of four representative novel ionizable lipids evaluated in this study. (C) Optimization scheme of iLNPs. DOE was used to minimize the number of formulation candidates based on each lipid from 256 to 16. As a result, 64 formulations in total were prepared and evaluated in this study on the basis of four novel ionizable lipids, with 16 formulations for each ionizable lipid. (D) Levels of each component of iLNP calculated by molar ratio. (E to H) In vitro gene silencing efficiencies of 4 panels (64 in total) of formulations prepared with A1-B3-7 (E), A1-D1-5 (F) A2-C1-8 (G), and A3-C1-8/D1-7 (H), respectively. Transfection concentration of siRNA was 50 nM. Four colors in pie charts of the x axis represent four lipids used in LNP formulations. Blue, proposed ionizable lipid; purple, DSPC; green, CHO; red, DMG-PEG2000. The area percentage of each color in the pie charts represents the molar percentage of the lipid in the formulation. (I) Transfection efficiencies of four leading formulations selected from panels of (E), (F), (G), and (H), respectively. The transfections concentrations nM, respectively. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.