Figure 4. Modularity of transposition and DNA targeting modules.
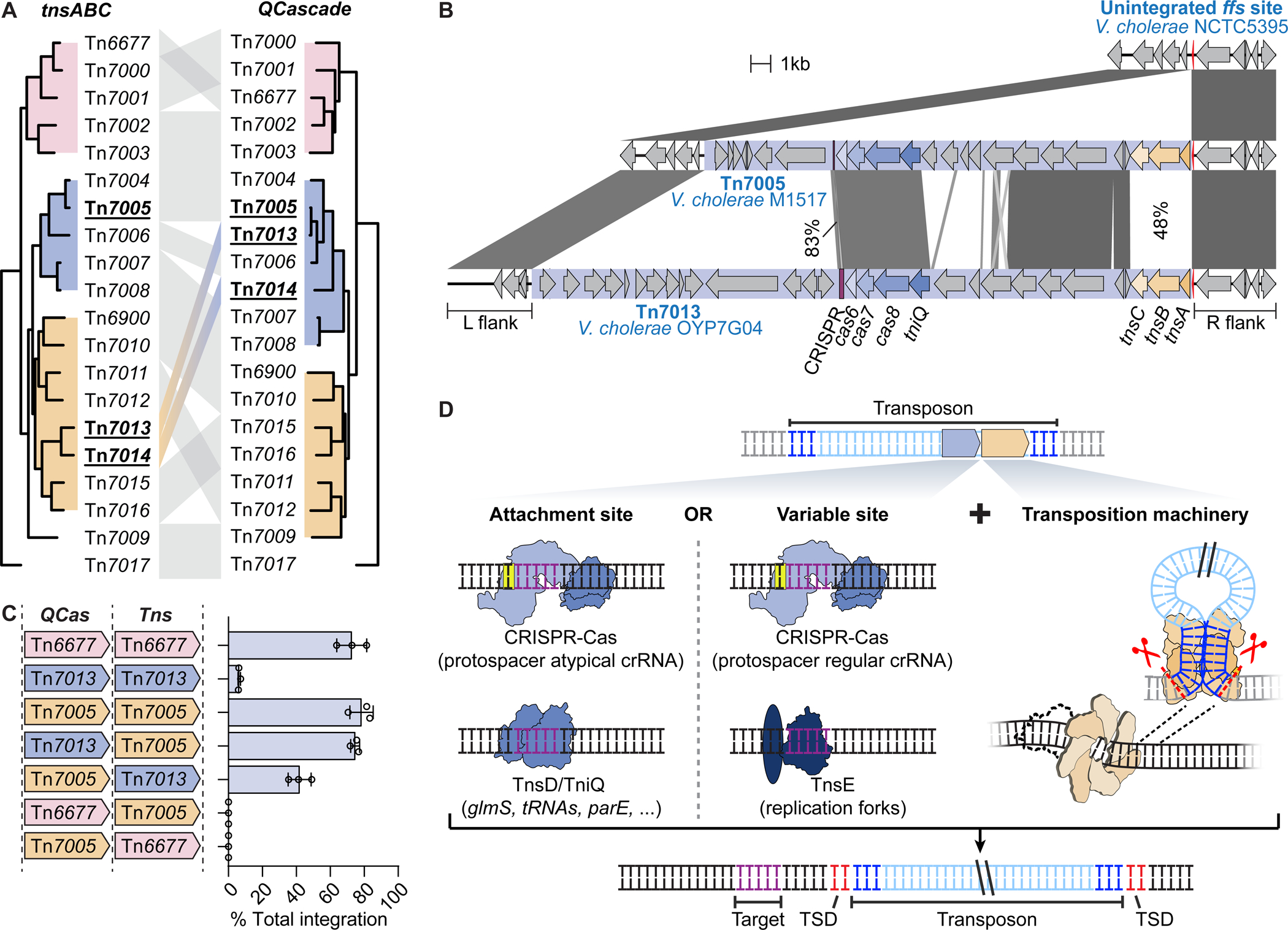
(A) Phylogenetic comparison of the tnsABC and tniQ-cas876 operons of CRISPR-Tn tested in this study. Tn7013 and Tn7014 show evidence of module exchange, in which a recombination event may have disrupted co-evolution of the transposition and DNA targeting modules. (B) Schematic representation of the sequence similarity between Tn7005 and Tn7013, both of which are found downstream of the ffs gene in separate V. cholerae strains. DNA sequence similarity is indicated for homologous regions. (C) Integration efficiency for different combinations of tniQ-cas876 (QCas) and tnsABC (Tns) operons from Tn6677, Tn7005, and Tn7013, as measured by qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. for n = 3 biologically independent samples. (D) Tn7-like transposons are modular in nature and encode homing pathways alongside flexible pathways that target mobile genetic elements. TSD, target site duplication. See also Figure S4.
