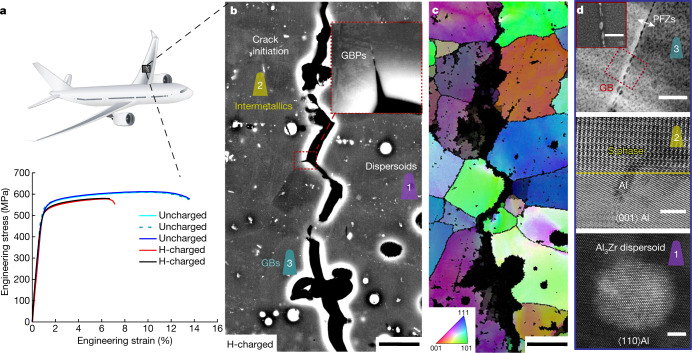
Fig. 1. Heterogeneous microstructure of an aerospace Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy.
a, Engineering stress–strain curves of uncharged and H-charged samples in the peak-aged condition (120 °C for 24 h). b, Backscattered electron imaging of an intergranular crack of the H-charged alloy subjected to tensile fracture. c, Electron backscatter diffraction imaging showing the crack along GBs. d, The microstructure of GBs, precipitates, PFZs31 and main types of secondary phases (the S phase47 and Al3Zr dispersoid). The colour schemes reflect the microstructures where specific APT analyses were performed. APT, atom probe tomography; GB, grain boundary; GBPs, grain boundary precipitates; PFZs, precipitate-free zones. Scale bars: 20 μm (b, c), 100 nm (d, top), 50 nm (d, top inset), 3 nm (d, middle and bottom).