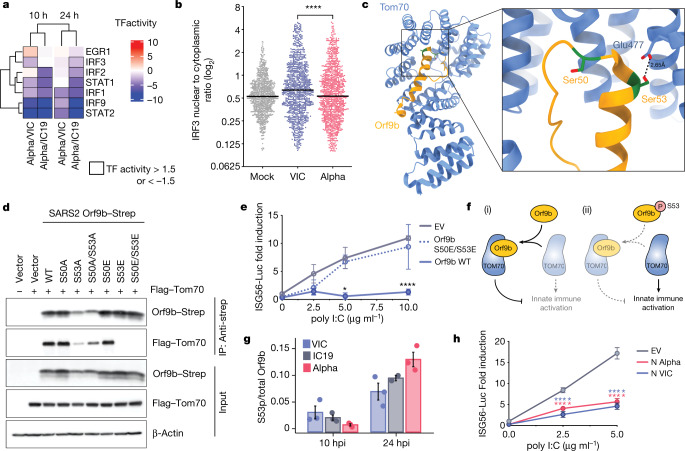
Fig. 4. Orf9b binds TOM70 and antagonizes innate immune activation downstream of RNA sensing.
a, Transcription factor (TF) activities in the five top enriched terms for the RNA-seq dataset (Fig. 2b, left); rows clustered hierarchically based on activity magnitude. Black outlines show activities >1.5 or < −1.5. b, IRF3 nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio measured by single-cell immunofluorescence at 24 h in cells infected at 2,000 E copies per cell; 1,000 randomly sampled cells per condition (cut-off of 0.1> = <5). c, Cryo-electron microscopy of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b (yellow) in complex with TOM70 (blue) (Protein Data bank (PDB) code: 7KDT)40. Serine residues (Ser50 and Ser53) in Orf9b in the TOM70-binding site are shown in red. d, Co-immunoprecipitation of Orf9b wild type (WT) or point mutants with TOM70 in HEK293T cells. e, ISG56-reporter activation by poly I:C in the presence of Orf9b WT, S50E/S53E or empty vector (EV) in HEK293T cells. f, Schematic of proposed innate immune antagonism by Orf9b. (i) When S53 is unphosphorylated, Orf9b binds TOM70 to inhibit innate immune signalling. (ii) When S53 is phosphorylated, Orf9b can no longer interact or antagonize innate immune activation. g, Ratio between the intensity of Orf9b peptide phosphorylated on Ser53 (S53p) and total Orf9b (as calculated in Fig. 3b, bottom) from phospho- and abundance proteomics of Calu-3 cells (Fig. 2). h, ISG56-reporter activation by poly:IC in the presence of N (VIC), N (Alpha) or EV in HEK293T cells. Mean ± s.e.m. Mann–Whitney test (b) or two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (e, h). For e, Orf9b WT versus Orf9b(S50E/S53E). For h, blue stars: VIC versus EV; red stars, Alpha versus EV. P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.