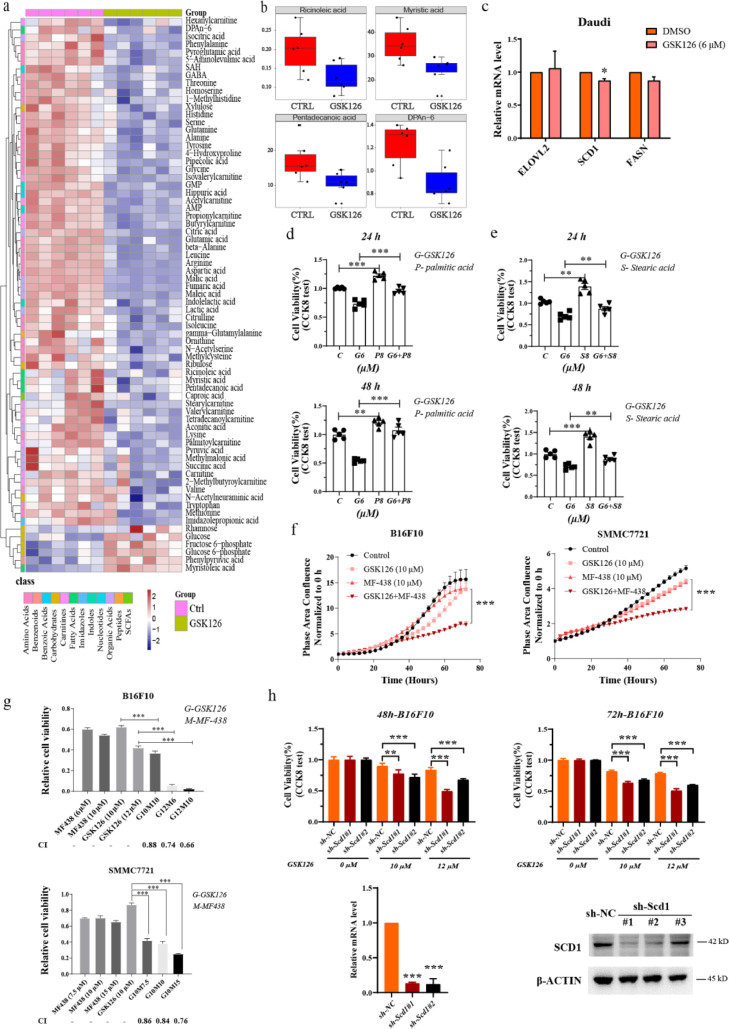
Figure 5.
Combination with SCD1 inhibitor enhanced the inhibitory effects of GSK126 on cancer cell. (a) Differential metabolites between Ctrl and GSK126-treated Daudi cells. Heat map shows the scaled abundance of 71 differential metabolites with VIP (variable importance in the projection) value greater than 1. The class of metabolites shows in different colors. (b) Four significantly decreased fatty acids in GSK126-treated Daudi cells. (c) mRNA level of lipid metabolism genes in GSK126 treated Daudi cells detected by real-time qPCR (n=3). (d) Cell viability of GSK126 and palmitic acid treated Daudi cells analyzed by CCK-8 kit (n=5). (e) Cell viability of GSK126 and stearic acid treated Daudi cells analyzed by CCK-8 kit (n=5). (f) Cell growth of GSK126 and MF-438 treated B16F10 and SMMC7721 cells monitored by IncuCyte S3. Mean ± SEM is shown (n=5). (g) Cell viability of GSK126 and MF-438 treated B16F10 and SMMC7721 cells detected by CCK-8 kit. CI was calculated by CompuSyn software. A CI < 0.9 indicates synergism and CI > 1.1 an antagonistic effect. (h) The effect of Scd1 knockdown to GSK126 treatment on B16F10 cells activity measured by CCK-8 assay. Mean ± SEM is shown (n=5). Scd1 mRNA and protein level after knockdown were detected by real-time qPCR and western blot. (d-f) analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison posttest. (c, g, h) analyzed by unpaired two-tailed t test, statistical comparisons are to control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.