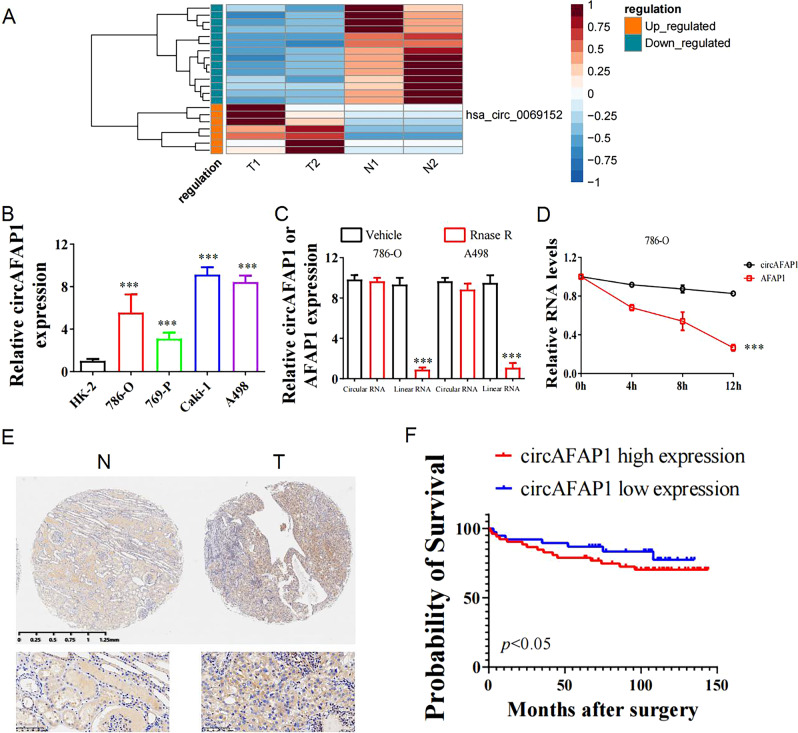
Fig. 1. circAFAP1 is upregulated in ccRCC and high expression of circAFAP1 predicted an unfavorable prognosis.
A Cluster heatmap for 21 deregulated circRNAs in two paired ccRCC and pericarcinomatous tissues (filtered by P < 0.05 and |FC (fold change)| ≥ 2). Columns represent tissues while rows for differentially expressed circRNAs, with circAFAP1 identified on the right of its rows. B qRT-PCR was analyzed for the expression of circAFAP1 in normal renal tubular epithelial cells line HK-2 and ccRCC cell lines 786-O, 786-P, Caki-1, and A498. Data were shown as the means ± SD. ***represents p < 0.001. C qRT-PCR was analyzed for expression of circAFAP1 and linear mRNA-AFAP1 in 786-O and A498 cells treated with or without RNase. Data were shown as the means ± SD. ***represents p < 0.001. D qRT-PCR detected the residual level of circAFAP1 and linear mRNA-AFAP1 in 786-O cells treated with Actinomycin D at the specific time point. Data were shown as the means ± SD. ***represents p < 0.001. E Tissue microarray data in 82 paired ccRCC and pericarcinomatous tissues stained by immunohistochemistry revealed circAFAP1 is upregulated in ccRCC tissue (Right panel) compared to pericarcinomatous tissues (Left panel). F Survival curves of 82 ccRCC patients with high or low expression, according to the immunohistochemical staining level and using the median value as the grouping criterion. The follow-up time spans 150 months after surgery.