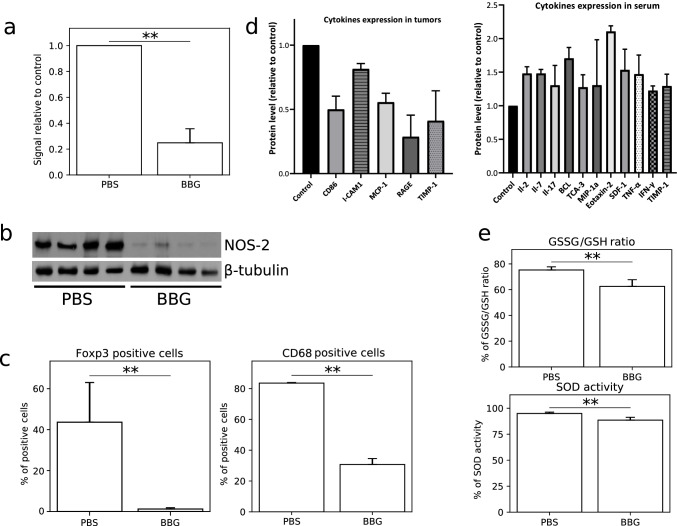
Fig. 6.
P2X7 inhibition reduced the ATP release with simultaneous decrease of some pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse serum and changed the redox metabolism in C6 tumors. a An ATP release is significantly lower in tumors treated with BBG compared to the control tumors (n = 4). The significance of the differences was determined using Student’s t-test: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. the respective control. b Decline NOS-2 expression in BBG-treated tumors (n = 4). c Decreased expression of FOXP3 (Treg lymphocytes) and CD68 (macrophages) markers in BBG-treated tumors evaluated using flow cytometry (n = 5). The significance of the differences was determined using Student’s t-test: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. the respective control. d The level of the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, in mouse serum and glioma tumors using cytokine array for multiplex protein detection (n = 3). e P2X7 inhibition caused a decrease of GSSG/GSH ratio with a slight decline of SOD activity in BBG-treated tumors (n = 4). The significance of the differences was determined using Student’s t-test: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. the respective control