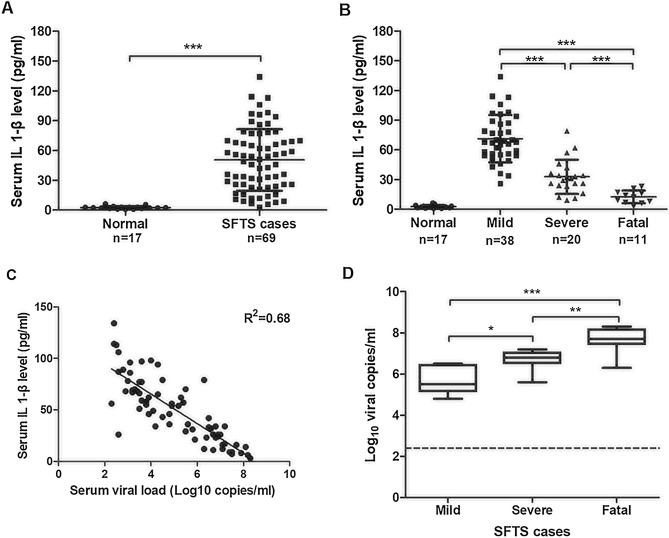
Figure 1.
Elevated IL-1β secretion in blood of the SFTS patients. (A) Increased IL-1β levels in the sera of patients (n = 69) and healthy individuals (n = 17) was determined by ELISA. Data shown were means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t-test). (B) IL-1β levels in the sera of the SFTS patients were negatively correlated to disease severity clinically. (C) Negative correlation was between the IL-1β levels and viral load in the sera of the SFTS patients. (D) The higher the serum virus titer in acute stage of SFTS cases, the more severe were the clinical symptoms. All serum samples were collected from SFTS patients on their second day of hospitalization. Viral load was determined based on the viral RNA copy numbers measured by RT-PCR with specific primers for the viral S genomic segment. R2 represented coefficient of the determination. r represented Pearson correlation coefficient, with r values of 0–0.3, 0.3–0.5 and > 0.5 indicating weak, moderate, and strong correlation, respectively.