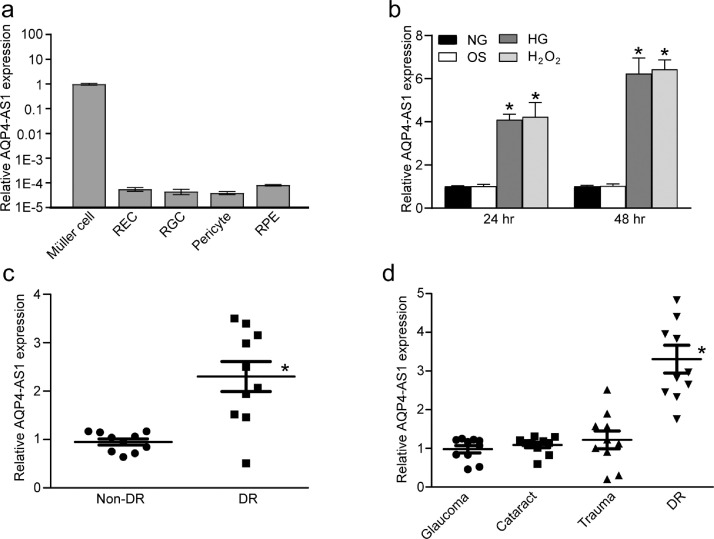
Fig. 1.
AQP4-AS1 level is significantly up-regulated under diabetic condition. (a) Quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCRs (qRT-PCRs) were performed to detect the levels of AQP4-AS1 in a wide array of retinal cells, including Müller cells, retinal endothelial cells (RECs), retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), pericytes, and RPE cells (n = 4). (b) qRT-PCRs were performed to detect the level of AQP4-AS1 gene in Müller cells after the following treatments for 24 h or 48 h, including normal glucose (5.55 mM, NG), 5.55 mM glucose + 24.45 mM mannitol (Osmotic control, OS), high glucose (30 mM, HG) or H2O2 (200 μM). *P < 0.05, n = 4, one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. (c) qRT-PCR assays were performed to detect AQP4-AS1 levels in the fibrovascular membranes of diabetic patients and idiopathic epiretinal membranes of non-diabetic patients (*P < 0.05, 2-tailed Student's t test). (d) qRT-PCR assays were performed to detect AQP4-AS1 levels in aqueous humor of patients with diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, cataract, or trauma (*P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test).