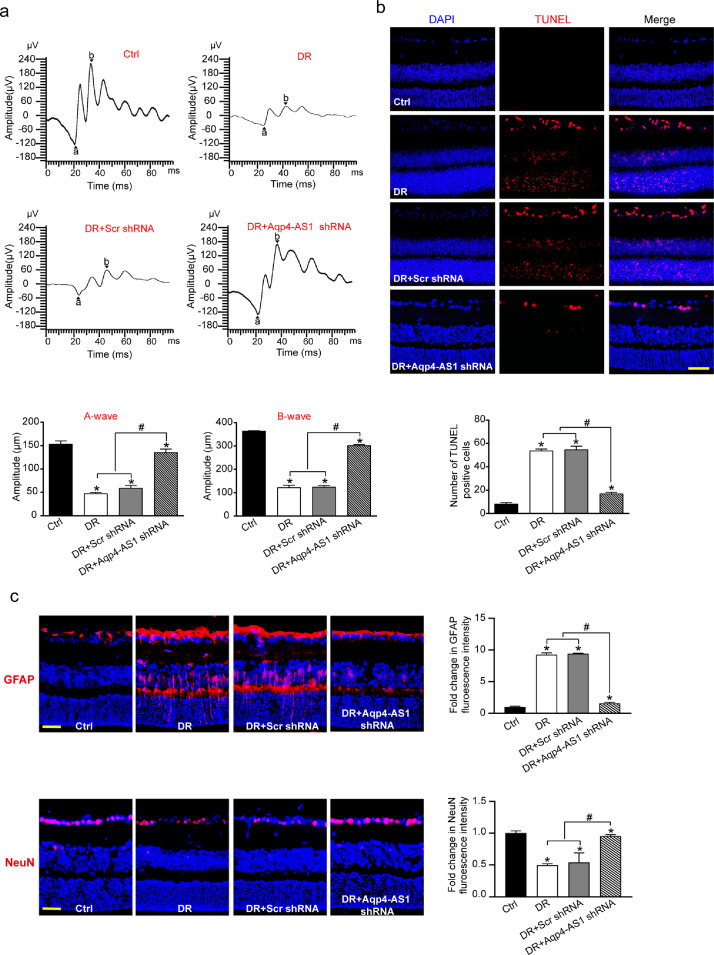
Fig. 4.
Aqp4-AS1 silencing protects against diabetes-induced retinal neurodegeneration. (a) Electrophysiology was conducted to detect the retinal function in non-diabetic mice (Ctrl), diabetic mice, Scr shRNA-injected, and Aqp4-AS1 shRNA-injected mice at 6-month after diabetes induction. Amplitudes of A and B waves were statistically analyzed (n = 6). (b) TUNEL assays and quantitative analysis was conducted at 6 months after diabetes induction (n = 6). Nuclei, blue; TUNEL-positive cells, red. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) Immunofluorescence and quantitative analysis of GFAP and NeuN staining were conducted to determine retinal reactive gliosis and RGC survival. The representative images were shown (n = 6). Scale bar, 50 μm. *P < 0.05 versus Ctrl group; #P < 0.05 DR+Aqp4-AS1 shRNA versus DR+Scr shRNA or DR. The significant difference was evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the post hoc Bonferroni test.