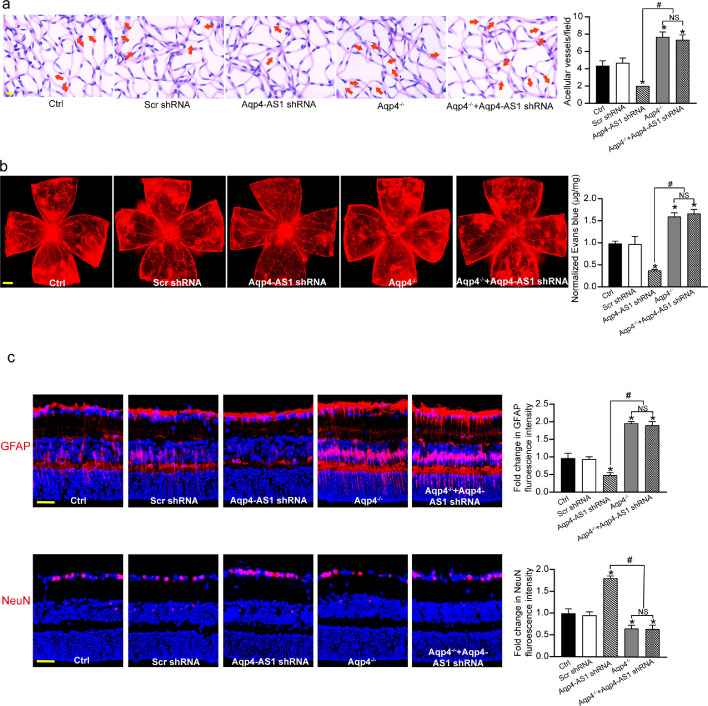
Fig. 7.
Aqp4/Aqp4-AS1 crosstalk is involved in the regulation of diabetes-induced neurovascular dysfunction. (a) Six months after diabetes induction, retinal trypsin digestion was conducted to detect acellular capillaries in diabetic retinas (Ctrl), diabetic retinas injected with Scr shRNA, Aqp4-AS1 shRNA, diabetic Aqp4 knockout mice (Aqp4−/−), and diabetic Aqp4 knockout mice (Aqp4−/−) injected with Aqp4-AS1 shRNA. Red arrows indicated acellular capillaries. Acellular capillaries were quantified in 30 random fields per retina and averaged (n = 6). Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) The mice were perfused with Evans blue dye for 2 h. The fluorescence signal of flat-mounted retina was detected using a fluorescence microscope. The representative images were shown. Meanwhile, the quantification of Evans blue leakage was conducted (n = 6). Scale bar, 200 μm. (c) Immunofluorescence analysis of GFAP and NeuN was conducted to detect retinal reactive gliosis and RGC survival. A representative image was shown (n = 6). Scale bar, 50 μm. *P < 0.05 versus Ctrl group; #P < 0.05 significant difference between the marked groups; NS, no significant difference. The significant difference was evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the post hoc Bonferroni test.