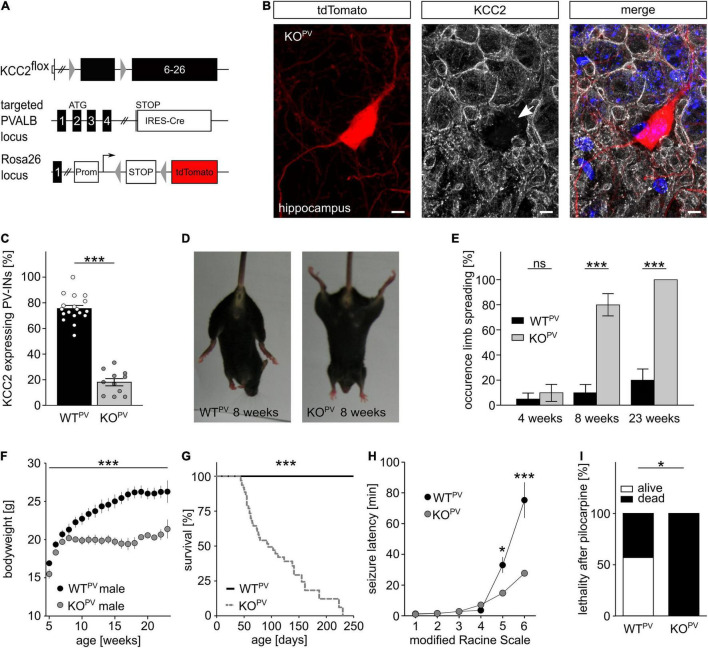
FIGURE 2.
Fatal epileptic activity upon disruption of KCC2 in PV-INs. (A–C) We mated our floxed Kcc2 line (Kcc2flox/flox) (Seja et al., 2012) with WTPV mice to delete exons 2-5 of the KCC2 gene (A). The KCC2-labeled section of an 8-week-old KCC2flox/flox/PV-Cre/tdTomato (KCC2 KOPV) mouse shows that the disruption of KCC2 was effective in the majority of tdTomato-labeled interneurons (arrow) (B). Scale bars 5 μm. The quantification of KCC2-labeled tdTomato-positive neurons in cortex of WTPV and KCC2 KOPV mice confirms the deletion of KCC2 in most PV-INs at 8 weeks of age (C). The ratio of tdTomato-positive with a clear plasma membrane labeling for KCC2 and the total number of tdTomato-positive cells was determined for the somatosentory cortex (WT: 75.5 ± 2.4%; KO: 18.1 ± 2.8%; quantification from n = 9 sections and N = 3 mice; Student’s unpaired t-test; ***p < 0.001). (D,E) KCC2 KOPV mice spread their hind limbs (D). Quantification of hind limb spreading in WTPV and KCC2 KOPV mice at different ages (N = 20/20 mice, Kruskal-Wallis Test; post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison; ns not significant; ***p < 0.001). (F) The gain in body weight is decreased in KCC2 KOPV mice (N = 10/9 mice; 2-way ANOVA; Bonferroni post-test; ***p < 0.0001). (G) KCC2 KOPV animals have a shortened life span with a mean survival of 94 days (N = 66/44 mice; Mantel-Cox Test; ***p < 0.0001). (H,I) 8-week-old WTPV and KCC2 KOPV mice were challenged with pilocarpine after LiCl sensitization to induce epileptic seizures. All challenged animals developed generalized tonic-clonic seizures. The seizure threshold was decreased in KCC2 KOPV mice compared to WTPV mice (N = 6/6 mice; 2-way ANOVA; Bonferroni post-test; ***p = 0.0003) and the seizure related lethality increased (I) (N = 6/6; 2-way ANOVA; Bonferroni post-test; *p = 0.037).