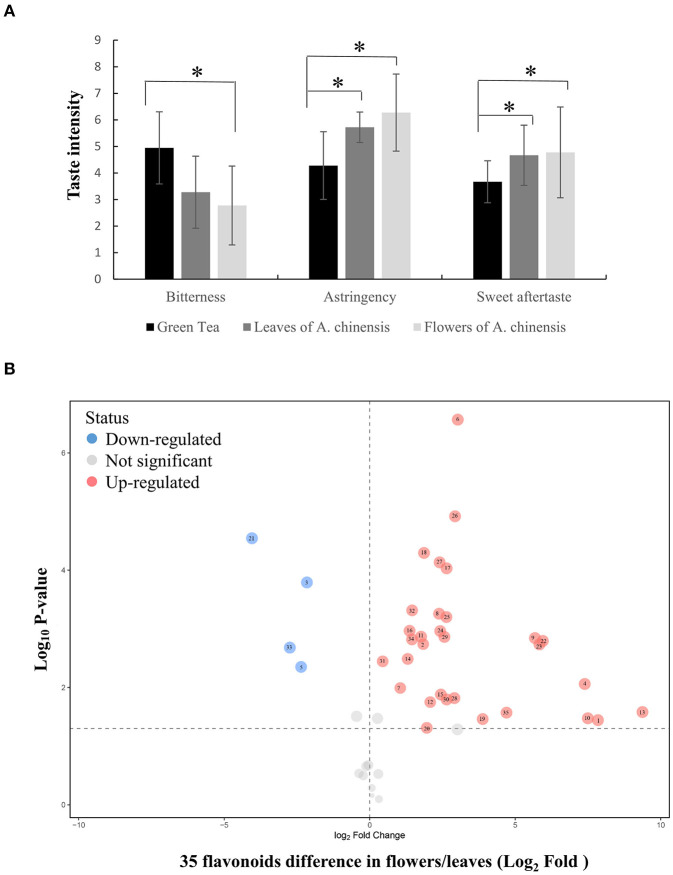
Figure 1.
Sensory evaluation and flavonoid profile of A. chinensis herbal tea. (A) The taste intensity of green tea, herbal tea madding from flowers and leaves of A. chinensis. (B) The flavonoid differential analysis between flowers and leaves. 1, (-)-Epigallocatechin; 2, Apigenin; 3, Astilbin; 4, Astragalin; 5, Avicularin; 6, Chalconaringenin; 7, Chrysin; 8, Cianidanol; 9, Cynaroside; 10, Dihydromyricetin; 11, Engeletin; 12, Galangin; 13, Gallocatechin; 14, Genkwanin; 15, Hyperoside; 16, isoliquiritigenin; 17, Isoquercitrin; 18, Isorhamnetin; 19, Isorhamnetin-3-O-nehesperidine; 20, Isosakuranetin; 21, Kaempferitrin; 22, Kaempferol; 23, Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside; 24, Myricitrin; 25, Narcissoside; 26, Naringenin; 27, Narirutin; 28, Phloretin; 29, Pinocembrin; 30, Procyanidin B1; 31, Procyanidin B2; 32, Quercetin; 33, Quercitrin; 34, Rutin; 35, Tiliroside. Data were statistically evaluated using Student's t test (*P < 0.05).